Figure 4. Examination of minor otoconins in the Oc90 wt and null vestibule.
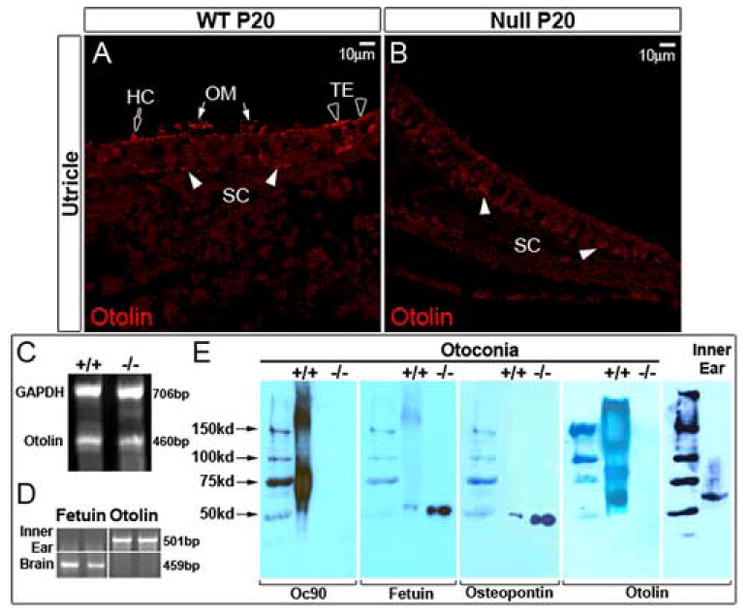
Otolin protein (60kD) is present in otoconial crystals (E) and membranes (OM) (arrows in A) and the pericellular matrix of hair cells (block arrow) and supporting cells (filled arrowheads) in the wt utricle and saccule (the utricle is shown). A few cells in the transitional epithelium (TE) have intracellular staining (unfilled arrowheads in A). However, otolin is absent (or greatly reduced to below the detection level) in the OM and giant crystals in the Oc90 null vestibule (B, E). Decalcified cross sections of the utricle and saccule were used for immunostaining with an antibody raised against the C-terminal unique peptide of murine otolin. Semi-quantitative multiplex RT-PCR detected expression of otolin mRNA in 1-month-old Oc90 wt and null inner ear epithelial tissues (C). Other minor otoconins, including fetuin-A and osteopontin, are present in the null crystals (E). Approximately 3.7 μg of wt and 5.1 μg of null otoconia protein was loaded. The same membrane was detected with antibodies against Oc90, fetuin-A (55 kD) and osteopontin (50 kD). Similar to collagen X, otolin forms extra-cellular multimers in otoconia crystals but exists as a monomer intra-cellularly in the inner ear epithelium. Also shown in (E) is confirmation of inactivation of Oc90 protein in null otoconia (1 month old) as examined by Western blotting using an antibody against the N-terminal peptide of the secreted protein. (D) Absence of fetuin-A (labeled as fetuin in D, E) and presence of otolin transcripts in the inner ear epithelium as determined by RT-PCR of tissues from C57 pups (P7) (assays were done in triplicates, but only duplicates are shown). The opposite is true in the brain: feuin-A transcript is present whereas otolin absent in the tissue. HC, hair cell; OM, otoconial membrane; SC, supporting cell; TE, transitional epithelium.
