Figure 2. CRT and CST tracing with DiI cortical injections.
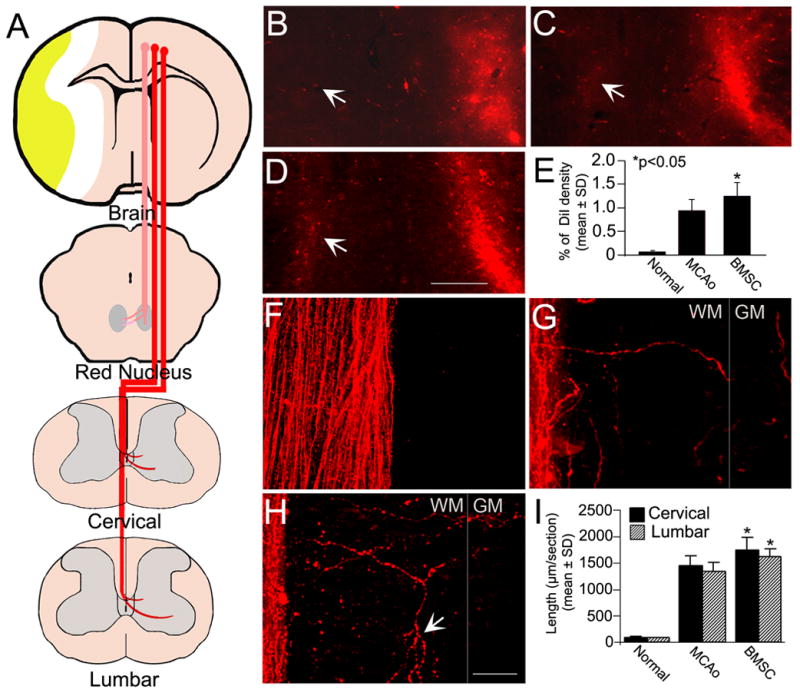
The CRT and CST arising from the left intact hemisphere were labeled by DiI cortical injections as shown in the schematic diagram (A). In normal rats, the CRT innervation was unilateral (B). Some CRT fibers changed their pathway to the lesioned red nucleus after stroke (C). Rats with BMSC treatment after stroke had an increased density of DiI-labeled fibers in the contralateral de-afferented red nucleus (D). Quantitation shows a significant CRT restructuring in BMSC treated animals as compared with controls (E, *p<0.05). In normal rats, no obvious axons crossed the midline into the opposite part of dorsal funiculus in a representative cervical longitudinal section (F). Four weeks after stroke, some DiI-labeled CST fibers were observed in the denervated side of the dorsal funiculus extending toward to the gray matter (G). The sprouting of branched CST axons from the intact side was enhanced by BMSC treatment postischemia (arrows in H). Compared with controls, the length of CST fibers was significantly increased in BMSC treated animals both in the cervical and lumbar cord (I, *p<0.05). WM: white matter, GM: gray matter. Scale Bar=250 μm in B–D, =25 μm in F–H.
