Figure 1.
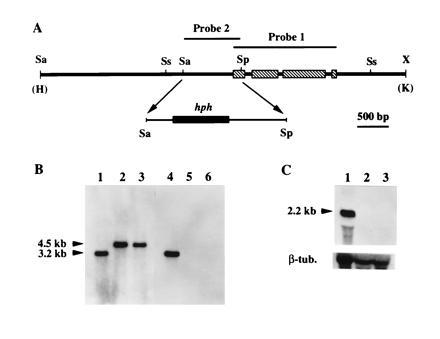
Disruption of cpg-1. (A) Map of the 7.1-kb HindIII/KpnI fragment derived from the cpg-1 disruption construct and used to transform C. parasitica spheroplasts. A 958-bp SalI/SphI fragment that contained 81 nt from the cpg-1 coding domain and the rest from the promoter region was replaced by a 2.3-kb DNA fragment containing the E. coli hph gene flanked by the A. nidulans trpC promoter and terminator (19). Probes used for Southern blot analyses are indicated above the map. The restriction endonuclease cleavage sites are: Sa, SalI; Sp, SphI; Ss, SstI; and X, XbaI. The HindIII (H) and KpnI (K) sites were from the cloning vector pUC18. (B) Results of Southern blot analyses for the cpg-1 disruptants. Total nucleic acid (10 μg) from the wild-type strain EP155 (lanes 1 and 4), and from cpg-1 disruptants G1-1 (lanes 2 and 5) and G1-15 (lanes 3 and 6) were digested with SstI, separated on a 0.8% agarose gel, and transferred to a Hybond-N membrane. DNA in lanes 1–3 was probed with a [32P]cDNA copy of the cpg-1 gene, indicated as probe 1 in A. In lanes 4–6, the blot was stripped and reprobed with a 32P-labeled 958-bp SalI/SphI fragment, indicated as probe 2 in A. The sizes of the expected hybridization bands are indicated at the left. (C) Results of Northern hybridization analyses of cpg-1 transcript accumulation in the wild-type strain EP155 (lane 1) and in cpg-1 disruption mutants G1-1 (lane 2) and G1-15 (lane 3). Total RNA (10 μg) was loaded in each lane, separated in a formaldehyde/1.4% agarose gel, and transferred to a Hybond-N membrane. The blot was hybridized with a [32P]cDNA copy of the cpg-1 gene (probe 1). The size of the transcript was indicated at the left. After autoradiography, the blot was stripped and rehybridized with a C. parasitica β-tubulin gene cDNA probe (16).
