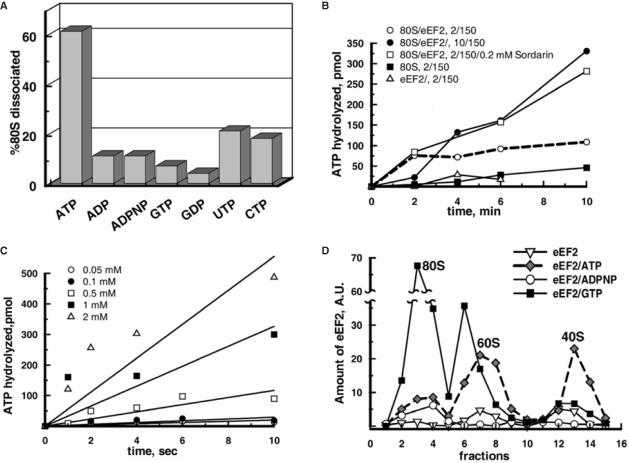
Figure 4.
ATP but not other nucleotides are essential for the eEF2-dependent dissociation of 80S ribosomes and the binding of eEF2 to subunits: ATP hydrolysis during the splitting. (A) Ribosomes (0.05 μM) were pre-incubated in buffer 2/150 with 2.5 μM eEF2 and 0.5 mM of one of the specified nucleotides for 6 min at 30°C and then eIF6 was added to 2 μM and further incubated for 15 min. The reaction mixtures were analyzed by SDGC. The percentages of dissociation of 80S ribosomes were determined as in Figure 3A. Standard error was ±5%. (B) Reaction mixtures (15 µl) containing 0.05 μM 80S ribosomes and 2.5 μM eEF2 were incubated at 30°C with 0.5 mM [γ-32P]ATP in buffer as indicated. Sordarin was purchased from Sigma. (C) Ribosomes were incubated with eEF2 as in (B) with indicated amounts of [γ-32P]ATP in buffer 2/150. (D) Ribosomes (0.05 μM) were incubated with eEF2 (1 μM) and 0.5 mM nucleotide as indicated in buffer 2/150 followed by treatment with 0.45% glutaraldehyde (v/v) and SDGC. The presence of eEF2 in each fraction was estimated by western blotting. In (B) and (C), each curve represents the average of three independent experiments.