Figure 1.
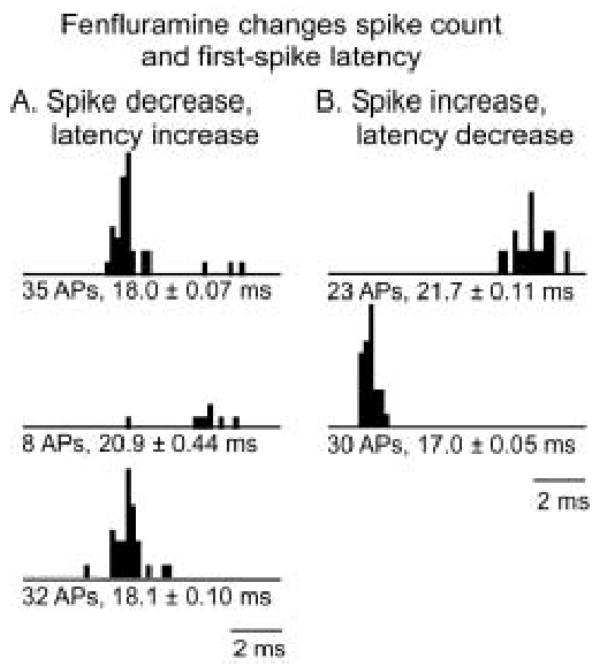
PSTHs of different effects of fenfluramine. A. Fenfluramine decreases spike count and increases first spike latency, with full recovery after the cessation of iontophoresis. The stimulus for this neuron was a 10 kHz FM sweep centered at 33 kHz, at 50 dB SPL. B. In another neuron, fenfluramine increased the spike count and decreased first spike latency. The stimulus presented to this neuron was a 10 kHz FM sweep centered at 25 kHz, at 10 dB SPL. Text below the PSTHs refer to spike counts and average first spike latencies ± S.E.M.; AP = action potential.
