Figure 5.
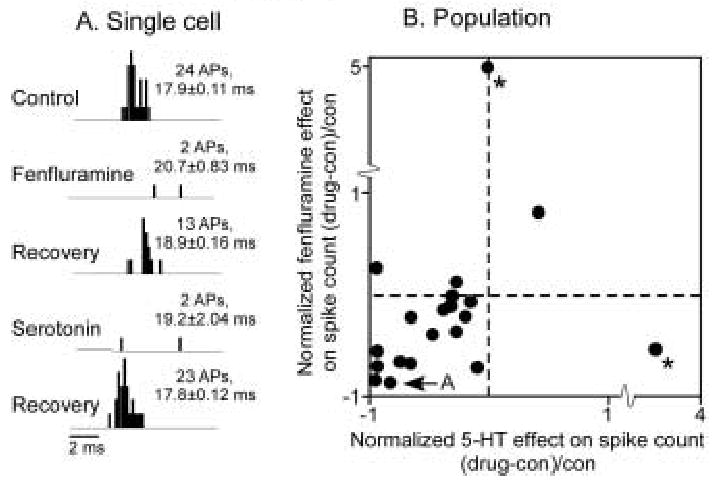
Comparison of the effects of fenfluramine and serotonin in the same neurons. A. PSTH of a neuron for which serotonin and fenfluramine both decreased spike counts. Spike counts partially recovered after the application of each drug. The stimulus for this neuron was a 10 kHz FM sweep centered at 23 kHz, at 50 dB SPL. B. Plot of normalized fenfluramine- and serotonin-evoked changes in spike count in 20 neurons to which both drugs were applied. Most neurons showed similar responses to fenfluramine and serotonin. Asterisks mark outliers. The regression including the outliers is not significant (p = 0.7; r2 = .009), but the regression excluding the two outliers is significant (p = 0.007; r2 = .37).
