Figure 7.
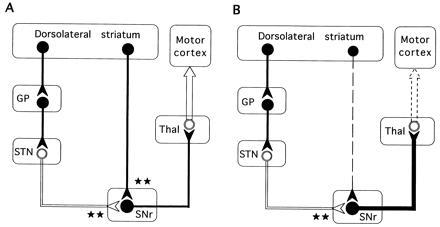
Simplified schematic representation of the basal ganglia–thalamocortical neuronal circuitry indicating the possible functional relationships underlying intrastriatal c-fos antisense induced akinesia-like symptoms. Inhibitory neurons (GABAergic) are shown as solid symbols, and excitatory neurons (glutamatergic) are shown as open symbols. ★, The degree of excitatory or inhibitory influence on the inhibitory nigrothalamic GABA pathway. (A) Untreated control. Two parallel and opposing GABAergic striatonigral (direct) and striatopallidal (indirect) pathways project from the striatum to the basal ganglia output nuclei and differentially regulate the inhibitory nigral projection to the thalamus. Striatal DA exerts contrasting effects on both of these pathways. DA has a net excitatory effect on striatal neurons that send GABA projections to the SN (the direct pathway) mediated by activation of D1 receptors, and a net inhibitory effect on those that send GABA projections to the GP (the indirect pathway) mediated by activation of D2 receptors (15, 34). Under normal conditions (A), activation of the striatonigral pathway facilitates movement by providing a positive feedback to the movement related neurons in the motor cortex through a reduced inhibitory GABA nigrothalamic influence, while activation of the opposing striatopallidal GABA pathway inhibits movements by providing negative feedback to the precentral motor fields by increasing the inhibitory GABA nigrothalamic influence. (B) Mechanism for the akinesia-like symptoms following acute intrastriatal injections of c-fos antisense oligonucleotide. The rapid decrease in nigral GABA release observed after the c-fos antisense oligonucleotide injection probably reflects reduction of impulse flow in the striatonigral GABAergic neurons (dashed line) leading to an increase in the inhibitory drive of the nigrothalamic GABA projections (thick black line) with a subsequent decrease in thalamocortical (motor cortex) glutamate transmission (dashed arrow). STN, subthalamic nucleus; Thal, thalamus.
