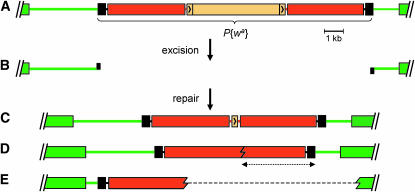
Figure 5.—
Gap repair assay using P{wa}. (A) Schematic of P{wa} structure. Green boxes represent exons of the sd gene. P{wa} is inserted into an intron of this gene. Black rectangles are P-element ends and red rectangles are the w gene. The copia retrotransposon (orange; LTRs indicated by carets) is inserted into an intron of w, decreasing expression such that homozygous females and hemizygous males have apricot-colored eyes, and hemizygous females have yellow eyes (Muller 1932). (B) Transposase-induced excision of P{wa} leaves a break that has 17-nt 3′ overhangs of P-element sequence. Most repair is believed to occur through SDSA (Kurkulos et al. 1994; Adams et al. 2003; McVey et al. 2004a,b). Completed SDSA can restore the entire P{wa} (not shown). (C) Completion of SDSA can also involve annealing of the copia LTRs, producing a P{wa} derivative that retains only one LTR; daughters that inherit this repair product have red eyes. (D and E) The major classes of inaccurate repair. In both cases, the w gene becomes nonfunctional, so daughters that inherit either of these chromosomes will have yellow eyes due to the single copy of P{wa} inherited from the mother. In D, repair is initiated by SDSA, but is completed by end joining rather than annealing of complementary sequences. In most such cases, synthesis occurs from both ends of the break, as shown here. The extent of synthesis from the right end (dotted double-headed arrow) can be estimated through molecular analysis. (E) In some cases of inaccurate repair, products have a deletion in sequences adjacent to the P{wa} insertion site. In this example, there has been synthesis from the left end of the break and deletion to the right side (dotted line). Deletions can also be bidirectional. When a deletion extends near or into an exon of sd, as depicted here, the result is a male-lethal allele of sd. Deletions are uncommon in wild-type males, but frequent in mus309 mutants.