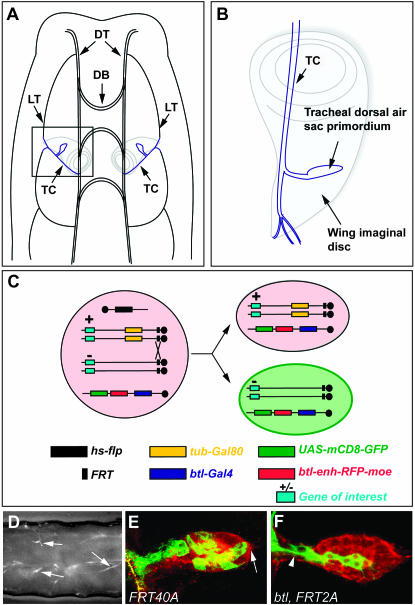
Figure 2.—
Localization of the dorsal air sac primordium in a Drosophila larva and generation and visualization of MARCM clones in the air sac primordium. (A) Schematic representation of the dorsal view of a Drosophila larva. The dorsal air sac primordium (blue) buds from a tracheal branch called the transverse connective (TC) and grows on the underlying wing imaginal disc (gray). DT, dorsal trunk; DB, dorsal branch; LT, lateral trunk; TC, transverse connective. (B) Schematic representation of the localization of a dorsal air sac primordium on the wing imaginal disc: magnification of the inset shown in A. (C) Schematic representation of the induction of MARCM clones. In all cells of animals heterozygous for the mutation of interest (+/−), the expression of the Gal80 repressor, which is under the control of a tubulin promoter, inhibits the Gal4-dependent expression of CD8-GFP. The expression of RFP-moesin is driven in all tracheal cells by the btl enhancer (red background). Upon heat-shock treatment of heterozygous animals, Flp expression is induced and drives the site-directed recombination at FRT sites, which ultimately leads, after mitosis, to the segregation of Gal80 and Gal4. The expression of CD8-GFP (green background) is therefore induced in cells homozygous for the mutation of interest (−/−). (D) GFP stereomicroscope view of a Drosophila larva of the F3 generation (see Figure 1B), after heat-shock treatment. Arrows indicate GFP-positive MARCM clones scattered in the tracheal system. Anterior is to the left, dorsal is up. (E and F) Confocal micrographs of a Drosophila third instar larval dorsal air sac primordium. All tracheal cells are labeled in red (RFP-moesin). Cells belonging to the MARCM clones are labeled in green (CD8-GFP). Clones are homozygous for a FRT40A (E) or btl, FRT42A chromosome (F). Arrows indicate the distal tip of the air sac primordium. Arrowheads indicate the proximal region of the air sac primordium.