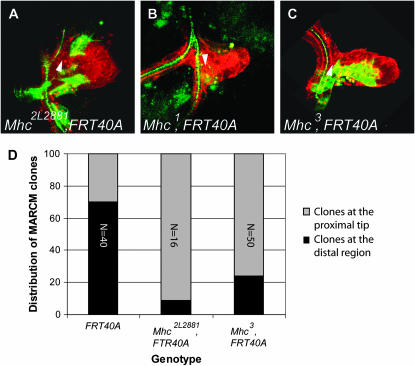
Figure 4.—
Homozygous Mhc mutant MARCM clones display a migration phenotype. (A–C) Confocal micrographs of a Drosophila third instar larval dorsal air sac primordium. All tracheal cells are labeled in red (RFP-moesin). Cells belonging to the MARCM clones are labeled in green (CD8-GFP). MARCM clones were induced in individuals heterozygous for Mhc2L2881 (A), Mhc1 (B), and Mhc3 (C). Arrowheads indicate the proximal region of the air sac primordium. (D) Graphical representation of the statistical distribution of MARCM clones in the dorsal air sac primordium (gray, localization at the proximal region; black, localization at the distal growing tip). The FRT40A chromosome was used as a wild-type control. Wild-type clones colonize the distal growing air sac tip in 70% of the cases. This proportion is dramatically reduced in the Mhc2L2881 and Mhc3 mutants. The numbers refer to the total number of observed clones.