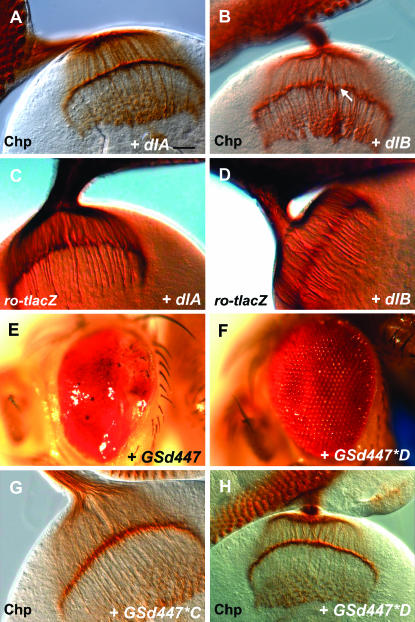
Figure 3.—
The effects of GSd447 are caused by misexpression of the dorsal gene. (A) Misexpression of Dorsal-A (GMR-GAL4/UAS-dlA) does not appear to result in an axon targeting defect when photoreceptors are stained using α-Chaoptin (Chp). Bar, 20 μm. (B) Misexpression of Dorsal-B (GMR-GAL4/+; UAS-dlB/+) causes gaps in the lamina (arrow) and thickened bundles that project into the medulla. (C) Using ro-tau-lacZ, some R2–R5 axons project past the lamina when Dorsal-A is misexpressed (GMR-GAL4/UAS-dlA). (D) Many R2–R5 axons mistarget past the lamina when Dorsal-B is misexpressed (GMR-GAL4; UAS-dlB/+). (E) GMR-GAL4/GSd447 flies have eyes that are small, misshapen, and glazed in appearance. Anterior is left and posterior is right. (F) Two mutagenized lines were identified in which these defects were suppressed and the eye returned to normal, as shown here in the case of GMR-GAL4/GSd447*D. (G, H) R-cell axon mistargeting is suppressed by mutations generated in genetic screen, shown here using α-Chaoptin (G,H).