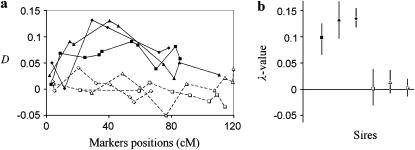
Figure 3.—
QTL analysis of multiple families with some nonshared markers. Six families with 2000 daughters each were simulated (three families with sire heterozygous for a single QTL situated at position 40 cM with allele substitution effect d/σ = 0.3 and three families with sire homozygous at the QTL). Chromosome length was 120 cM with 6–10 markers per family; a proportion 0.10 of all daughters was selected to each tail in each family. Individuals in both tails were randomly subdivided into four sub-pools. (a) D-value across the markers for each family (solid and open squares, triangles, and diamonds represent D in families with QTL-heterozygous and -homozygous sires correspondingly); (b) the results of jackknife resampling analysis (90% confidence intervals of λ-values for each family are shown by vertical lines, estimated in 500 jackknifes). The experimentwise P-value in a permutation test based on Σ(λf)2 was 0.012 (in 1000 permutations). The corresponding experimentwise permutation test P-values per family were 0.018, 0.012, 0.023, 0.483, 0.344, and 0.428 Estimated QTL position on all six families or on three families with a significant (P-value <0.05) λ-value was 43.9 cM (SD = 2.8) and 43.6 (SD = 2.6) cM, respectively. Estimated power for P-value = 0.05 was 99%.