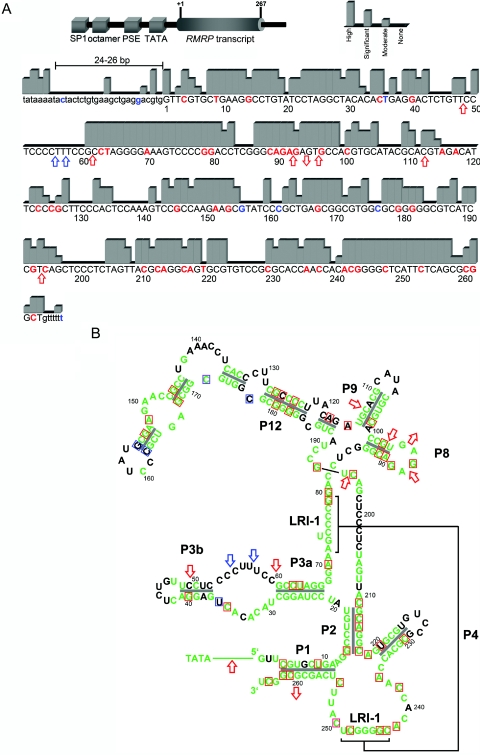
Figure 2. .
A, Schematic drawing of RMRP (top) and degree of RMRP evolutionary conservation (bottom), categorized into four levels by sequence alignment of nine species. The length between the TATA box and the transcription start site is conserved at 24–26 bp. This distance is known to be important for proper binding of the RNA polymerase III transcription factor complex (TFIIIB) and is altered by insertions, duplications, and triplications, leading to reduced transcription.9,17,18 SP1 = SP1 binding site; octamer = octamer element; PSE = proximal sequence element. Nucleotides for which disease-related mutations have been published are in red; polymorphic sites are in blue. B, Mapping of evolutionary conservation of RMRP nucleotides to its two-dimensional structure.4 Green indicates moderately to highly conserved nucleotides. Nucleotides for which disease-related mutations have been published are boxed in red; polymorphic sites are boxed in blue. Red arrows indicate insertion or deletion mutations; blue arrows indicate insertion or deletion polymorphisms. Note that disease-related mutations, which do not affect conserved nucleotides, lead to mispairing in stem structures.