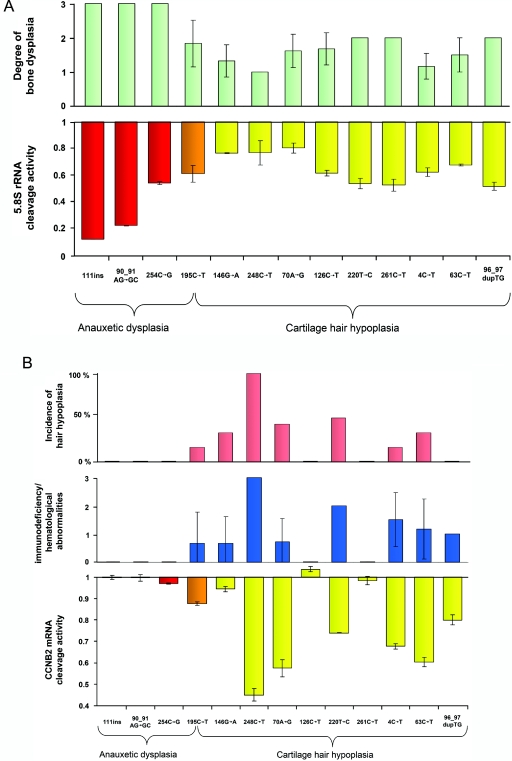
Figure 3. .
Correlation of phenotype scores for mutations analyzed, with reference to degree of bone dysplasia, hair hypoplasia, and immunodeficiency/hematological abnormalities. A, Results of 5.8S rRNA cleavage activity normalized to wild-type activity as a function of ribosomal assembly in 13 mutations, compared with the respective skeletal phenotype score, revealing a significant negative correlation between degree of bone dysplasia and rRNA cleavage activity (R=-0.8346; P=.0008). rRNA cleavage was most affected by the AD mutations g.111_112insACGTAGACATTCCT and g.90_91AG→GC. An intermediate effect was observed for the AD mutation g.254C→G; mutation g.195C→T, identified in the new patient with AD as well as in patients with CHH and MDWH; and mutations g.126C→T, g.220T→C, g.261C→T, g.4C→T, g.63C→T, and g.96_97dupTG, leading to the milder phenotypes. The least effect was seen for g.146G→A, g.248C→T, and g.70A→G. Red columns represent AD mutations, yellow columns represent CHH and MDWH mutations, and orange columns represent AD, CHH, and MDWH mutations. B, Results of mRNA cleavage activity normalized to wild-type activity as a function of cell-cycle progression in 13 mutations, compared with the respective immunological/hematological phenotype score and the incidence of hair hypoplasia. Notably, the presence of impaired mRNA cleavage activity strongly correlates with the immunological/hematological phenotype and the likelihood of hair hypoplasia (R=-0.8429 [P=.0007] and R=-0.8115 [P=.001], respectively).