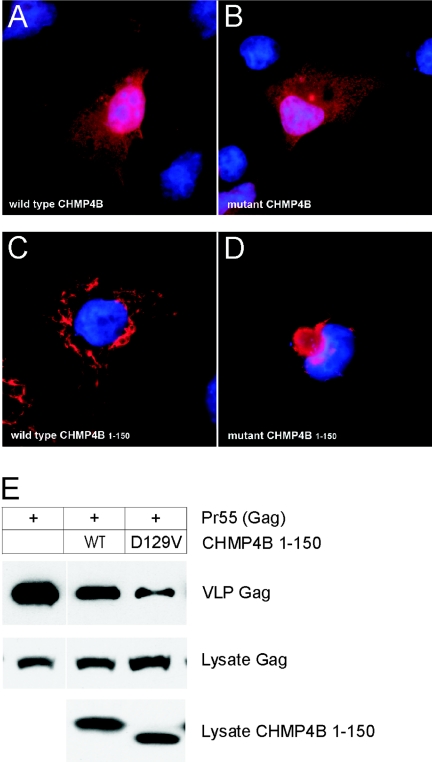
Figure 6. .
Transient expression of CHMP4B in cultured cells. A–D, Subcellular localization of CHMP4B proteins in COS-7 cells, visualized by immunostaining with FLAG antibody and epifluorescence microscopy. A, Full-length wild-type FLAG-CHMP4B. B, Full-length mutant FLAG-D129V-CHMP4B. C, Truncated wild-type FLAG-CHMP4B1–150. D, Truncated mutant FLAG-D129V-CHMP4B1–150. For full-length constructs, the coding sequence (codons 1–224) of human CHMP4B was PCR amplified from HeLa cDNA (Clontech) with forward (5′-gtagatctatgtcggtgttcgggaagctgttcgg-3′) and reverse (5′-cactcgagttacatggatccagcccagttctcc-3′) primers and then subcloned into the BamHI and XhoI restriction sites in the poly-linker of pcDNA3.1-FLAG.46 The D129V substitution was generated using the QuickChange mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). For truncated CHMP4B constructs, amplicons corresponding to codons 1–150 were amplified using the full-length constructs as templates and were subcloned into pcDNA3.1-FLAG as above. Plasmid DNA was prepared using the QIAprep spin kit (Qiagen), and inserts were verified by sequencing using the T7 primer. For transient expression, cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Gibco-BRL) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (Gibco-BRL), 5% supplemented calf serum (Hyclone Laboratories), and 2 mM glutamine. Cells were transfected with expression plasmids by use of Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen). At 18–24 h after transfection, COS-7 cells grown on glass cover slips were fixed in 3.5% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized in 0.2% Triton X-100, and immunostained with rabbit FLAG antibody (Sigma) followed by Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (Molecular Probes). Cell nuclei were counterstained (blue) with DAPI (4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole [Molecular Probes]). E, Immunoblot analysis of VLPs produced by HEK 293T cells cotransfected with plasmids encoding Gag (p24 antibody) and CHMP4B1–150 (FLAG antibody). Top blot shows Gag recovered in VLPs, and middle blot shows Gag in cell lysates. Bottom blot shows that the levels of CHMP4B1–150 were similar in cell lysates; however, the D129V substitution increased the electrophoretic mobility of the mutant fragment on SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) polyacrylamide gels compared with its wild-type counterpart. For VLPs, HEK 293T cells were transfected with 4 μg pCMV55 encoding HIV Gag, alone or together with 1μg of the indicated CHMP4B construct. At 18–24 h after transfection, media containing VLPs was harvested and clarified by passing through a 0.45 μm filter. VLPs were pelleted by centrifugation (3 h) through a 20% sucrose cushion at 26,000 rpm in SW41 Ti rotor (Beckman Coulter). VLPs and cell lysates were resuspended in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer, were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and then were analyzed by immunoblotting using rabbit antibody against p24, the capsid domain of HIV Gag, horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, and the SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescence detection kit (Pierce). Immunoblot signals were quantified using the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (Li-Cor Bioscience).