Fig. 3. Pax6 is required for RSC sphere formation in adult animals.
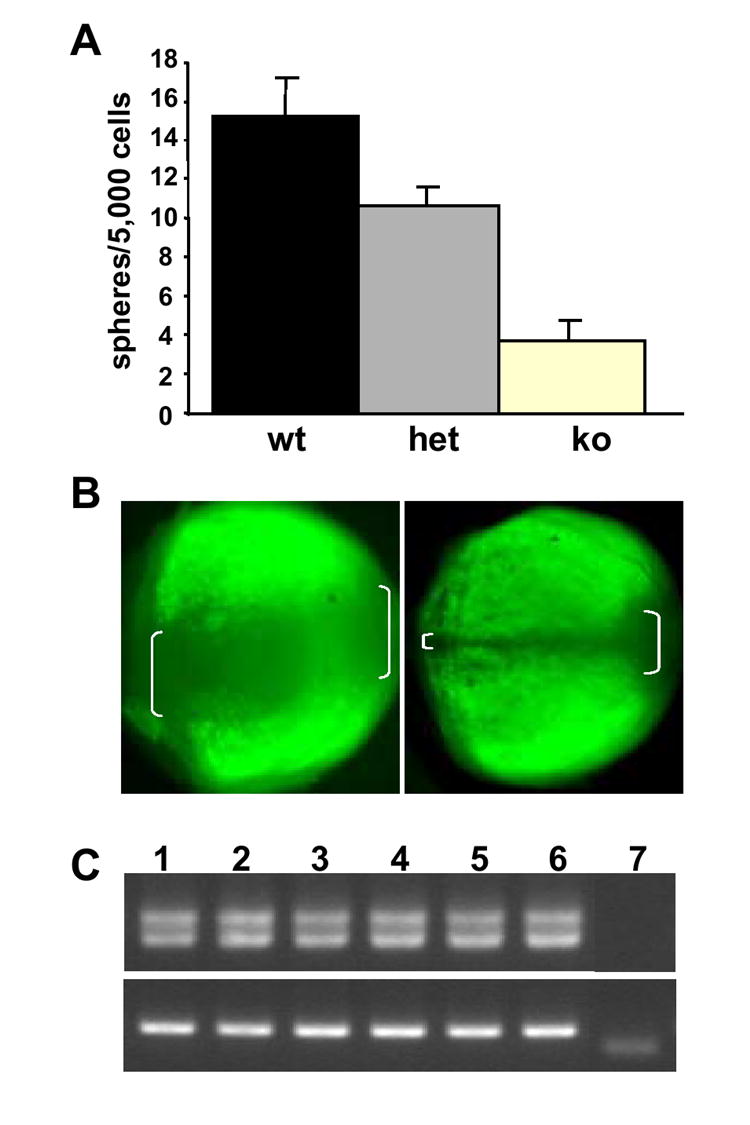
A. RSC sphere assays in the Pax6 conditional knockout mouse model (Marquardt et al., 2001). ko: α-Cre +/-; Pax6loxP/loxP (n=4). het: α-Cre +/-; Pax6loxP/wt (n=4). wt: α-Cre -/-; Pax6wt/wt (n=4). B. whole mount fluorescent images of adult α-Cre, Z/EG mouse eyes showing the α-promoter-driven expression has gaps (marked by white brackets) as seen from dorsal (left) and ventral (right) views of the retina. Anterior is on the left. C. RT-PCR of Pax6 on the clonal RSC spheres derived from adult α-Cre; Pax6loxP/loxP ciliary epithelial cells. The same primers, encompassing the alternatively spliced exon 5a were used. 1: wild type single RSC sphere; 2-6: RSC spheres derived from α-Cre; Pax6loxP/loxP CE cells, 7: negative control (amplification without reverse transcription).
