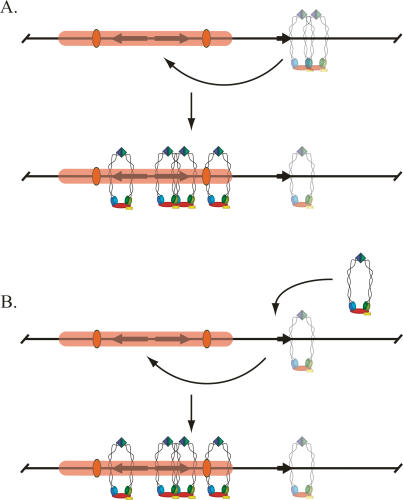
Figure 8.
Models for the role of tT(AGU)C in cohesion of HMR. (A) tT(AGU)C activates a nonfunctional pool of cohesin on the adjacent tpx1 and tpx2 sites (represented as a translucent complex) that then migrates to the neighboring silenced chromosomal domain. (B) tT(AGU)C loads an active pool of cohesin, which then migrates to the adjacent silenced chromosomal domain. Silencing-dependent cohesin has thus far been detected on the a2 gene (Fig. 4), the a1 gene, and the HMR-I silencer (Chang et al. 2005).