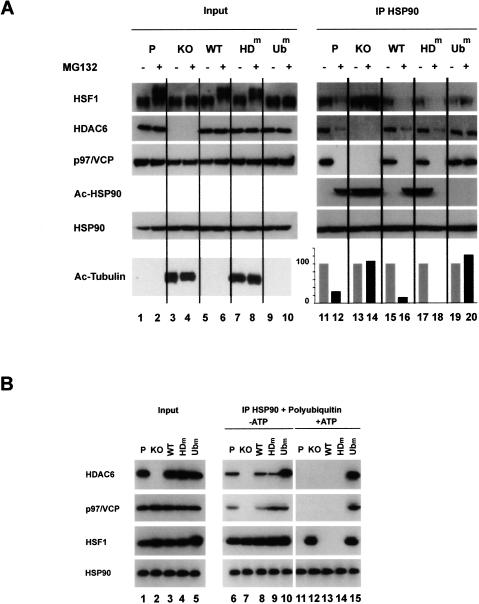
Figure 3.
A treatment with MG132 leads to an HDAC6-dependent dissociation of the repressive HSP90–HSF1 complex. (A) Extracts from the different cell lines described in Figure 1A treated for 6 h (+) with MG132 or untreated (−) were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HSP90 antibody, and the coimmunoprecipitation of HSF1, p97/VCP, and HDAC6 was monitored. The acetylation of the immunoprecipitated HSP90 was also detected using an anti-acetylated lysin antibody. The “input” panel shows the presence of the studied proteins before immunoprecipitation in the extracts. (Right panel) The amount of HSF1 coimmunoprecipitated with HSP90 was estimated by densitometric measurement of HSF1 signals before and after MG132 treatment (shown in the HSF1 lane) and is represented as histograms. The values are expressed as a percent of HSP90-associated HSF1 before the MG132 treatment in each cell line. (B) HSP90 immunocomplexes obtained after the immunoprecipitation of HSP90, as described in A, were incubated with 10 μg of pentaubiquitin chain in the presence of 2 mM ATP/2 mM MgCl2 or not. After the elimination of the supernatant, the proteins remaining associated with the HSP90 immunocomplex were analyzed by Western blot.