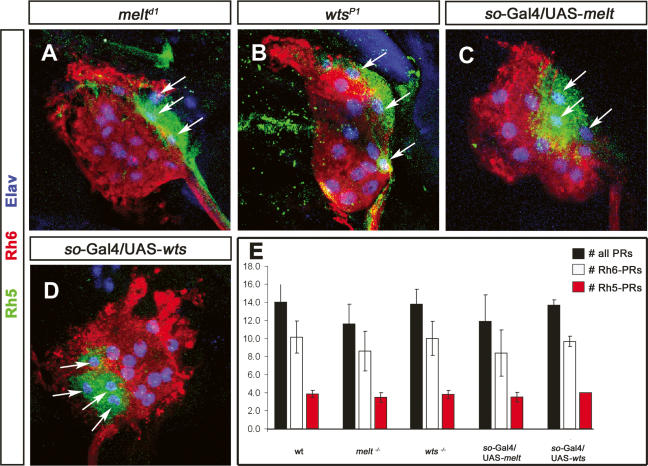
Figure 2.
wts and melt are not involved in Rh5- and Rh6-subtype specification. High-magnification images of third instar mutant larva BO of melt (A), wts (B), so-Gal4/UAS-melt (C), and so-Gal4/UAS-wts (D) labeled with anti-Rh5 (green, arrow), anti-Rh6 (red), and anti-Elav (blue). (A–D) melt and wts mutants, as well as so-Gal4/UAS-wts and so-Gal4/UAS-melt, display an expression of Rh5 and Rh6 PRs comparable with wild-type larvae. (E) Comparison of the total number of PRs (black bar) and Rh6 (white bar) and Rh5 (red bar) PRs in wild-type (wt), melt LOF, wts LOF, melt GOF, and wats GOF larval eyes (error bars, SD). The number of total PRs and Rh5 and Rh6 PRs in all conditions are comparable with wild type.