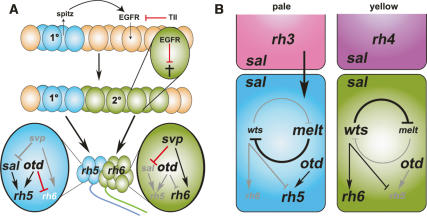
Figure 8.
Proposed model for development and the specification of rhodopsin fates in the larval eye and comparison with the adult R8. (A) Primary precursors (1°, blue) express the TGFα homolog spi, which is required in secondary precursor cells (2°, green) for their survival. tll acts in the surrounding tissue to inhibit secondary precursor development. Primary precursors give rise to the Rh5 PR subtype, whereas secondary precursors give rise to the Rh6 PR subtype. In the Rh5 PR subtype, sal and otd are required for Rh5 expression, and otd further for the repression of Rh6. In the Rh6 subtype, svp is required for Rh6 expression and for the repression of sal expression. (B) The negative feedback loop of wts and melt mediates the decision of R8 to express Rh6 or Rh5. Which way the loop swings depends on an instructive signal of the overlying R7 cell. The presence of gene expression is indicated by black type and its absence is indicated with gray type. Arrows shown in black (for activation) and red (for repression) indicate an active interaction; gray arrows indicate the absence of this interaction.