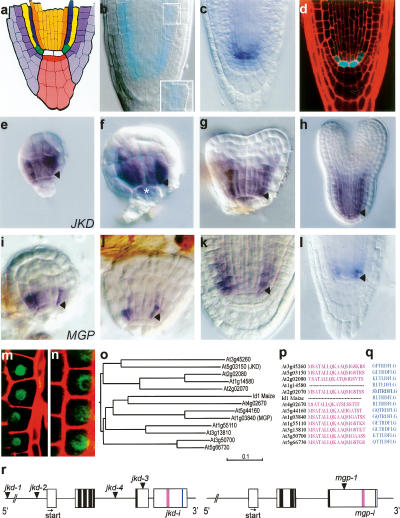
Figure 1.
JKD encodes a C2H2 zinc finger expressed in the QC and ground tissue. (a) Median longitudinal view of the Arabidopsis root meristem (RM). (White) QC; (red) columella stem cells; (pink) columella root cap; (light purple) lateral root cap; (purple) epidermis; (green) cortical/endodermal stem cells; (yellow) cortex; (blue) endodermis; (orange) pericycle; (light orange) provascular cells. (b) GUS staining of the DWK15 promoter trap line (jkd-1) at 3-dpg; inset shows ectopic periclinal cortex division. (c) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with a JKD probe in 3-dpg wild-type Col-0 seedling. (d) Longitudinal confocal section of pJKD∷CFP. (e–h) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with JKD in wild-type 32-cell stage (e), globular stage (f), early heart stage (g), and torpedo stage (h) embryos. (i–l) MGP expression during embryogenesis (i–k) and in 3-dpg wild-type seedlings (l). Arrowheads mark cortex/endodermis stem cells. Asterix marks the QC cells. (m,n) Longitudinal confocal section of 35S∷JKD:GFP and 35S∷MGP:GFP in Arabdidopsis root epidermal cells. (o) Phylogenetic tree of JKD/ID1 protein family. (p,q) Amino acid sequence alignment of conserved C-terminal domains. (r) Schematic representation of JKD and MGP genes. Dark boxes indicate location of zinc finger domains, pink and blue boxes indicate conserved C-terminal domains. Arrowheads mark the site of T-DNA insertions, arrows mark the translation start.