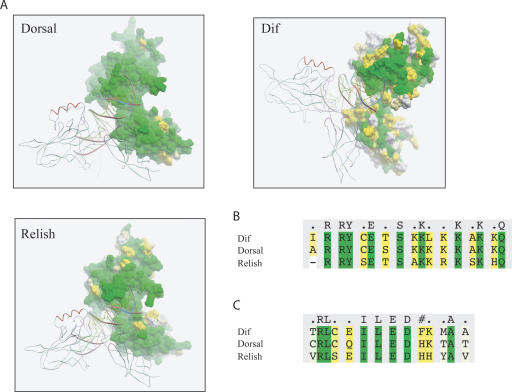
Figure 1.
Conservation of amino acid residues involved in DNA recognition and protein dimerization. (A) Molecular modeling of Drosophila Rel homodimers bound to DNA. One subunit of Rel homodimer is represented as a molecular surface, while the second subunit and DNA are shown as ribbons. (B) Alignment of DNA-binding residues of Dorsal, Dif, and Relish from D. melanogaster. (C) Alignment of dimerization residues of Dorsal, Dif, and Relish from D. melanogaster. Molecular surface and amino acid residues are colored according to their conservation: green color indicates fully conserved residues; yellow marks conservative substitutions, and white, nonconserved residues.