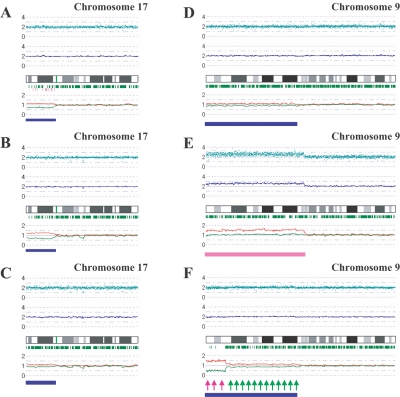
Figure 4. .
Detection of AI in samples of primary AML and MPD. AsCN analyses disclosed the presence of a small population with 17p UPD in a primary AML specimen (W150673) (93% blasts in microscopic examination) with either a paired sample (A) or anonymous reference samples (B). The difference of the mean CNs of the two parental alleles is statistically different between panels A (0.38) and B (0.55) (P<.0001, by t test), which is explained by the residual tumor component within the bone marrow sample in complete remission (1% blast) used as a paired reference (W150673CR) (C). AI in the 9p arm was also sensitively detected in JAK2 mutation–positive MPD cases. UPD may be carried only by a very small population (∼20% estimated from the mean deviation of AsCNs in 9p) (IMF_10) (D), or by two discrete populations within the same case (PV_06), as indicated by two-phased dissociation of AsCN graphs (pink and green arrows) (F). AI in 9p is mainly caused by UPD but may be caused by gains of one parental allele without loss of the other allele (E), both of which are not discriminated by conventional allele measurements. Blue and pink bars are UPD and AI calls, respectively, from the HMM-based LOH detection algorithm. Other features are identical to those indicated in figure 1.