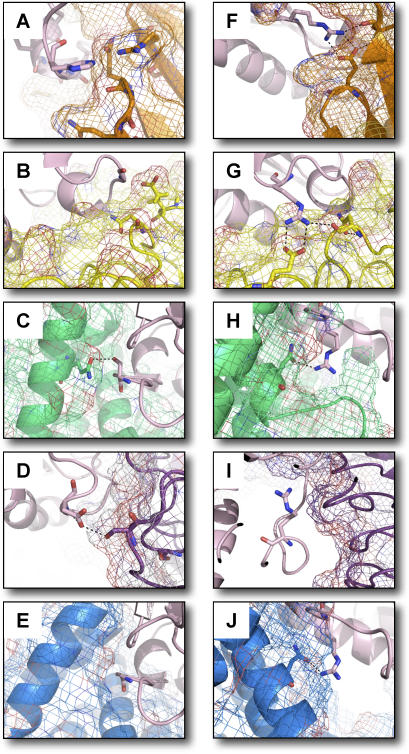
Figure 4. Single- and Multi-Constraint Models for Two Ran Interface Sites.
Shown are computational models of interface regions around residues predicted to be optimal for binding each partner (orange, 1A2K.pdb; yellow, 1I2M.pdb; green, 1IBR.pdb, purple, 1K5D.pdb; blue, 1WA5.pdb) of Ran (pink). Single-constraint predictions for residue 74 (A–E) (wild-type glycine) indicate compromise among the preferences of the five partners. Three partners (A,C,D), when optimized alone, prefer a residue with greater hydrogen bonding capabilities than the wild-type glycine. Steric constraints imposed by the remaining two partners (B,E) forced selection of the wild-type glycine by the multi-constraint protocol. Multi-constraint predictions for residue 76 are shown in panels F–J. The wild-type arginine is also chosen in all single-constraint predictions where it mediates an inter-chain hydrogen bonding network (F,G,H,J). Single-constraint selection of leucine at position 76 for 1K5D.pdb is not shown.