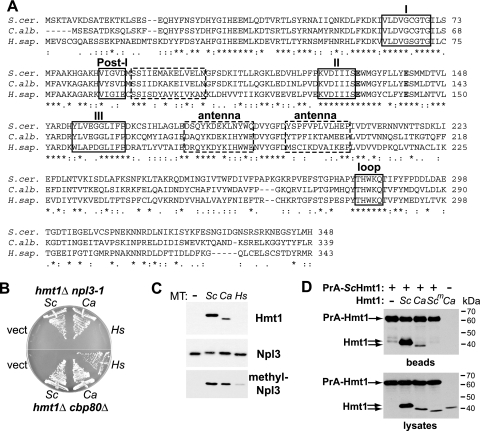
FIG. 1.
Hmt1 is functionally conserved between S. cerevisiae and C. albicans. (A) Clustal W alignment (9) of type I arginine methyltransferase proteins Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hmt1 (S. cer.), Candida albicans Hmt1 (C. alb.), and human PRMT1 (H. sap.) HRMT1L2v.1 (35). Indicated motifs include conserved methyltransferase motifs (I, post-I, II, and III) that mediate binding to the enzyme cofactor AdoMet, double-E (bold) and THW loop motifs common to protein methyltransferases, and the “antenna” domain (positions 175 to 204) that mediates dimerization of S. cerevisiae Hmt1 through hydrophobic interactions with the AdoMet-binding domain (dashed boxes) (44). Asterisks denote identical residues in all sequences, colons denote conserved substitutions, and periods denote semiconserved substitutions. (B) S. cerevisiae strains that require HMT1 due to the presence of the npl3-1 mutation (PSY866) or deletion of the 80-kDa cap-binding protein gene (PSY1191) were transformed with CEN LEU2 plasmids that express either no Hmt1 (vector, pRS315) or one of the arginine methyltransferases shown in panel A (Sc, S. cerevisiae Hmt1, pPS1872; Ca, C. albicans Hmt1, pAM160; Hs, H. sapiens PRMT1, pAM161). The functionality of each methyltransferase was tested by incubation on medium containing 5-FOA, which selects for loss of a URA3 ScHMT1 expression plasmid, at 25°C (hmt1Δ npl3-1) or 30°C (hmt1Δ cbp80Δ) for 3 days. (C). An hmt1Δ S. cerevisiae strain (PSY865) was transformed with the plasmids described for panel B, and grown at 30°C to mid-log phase, and lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer. Total protein (5 μg) was analyzed by immunoblotting with polyclonal antisera raised against ScHmt1 (27) and ScNpl3 (7) from S. cerevisiae and a monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes methylated ScNpl3 (1E4) (38, 46). (D) A PrA fusion to S. cerevisiae Hmt1 (+) was expressed from pAM91 in cells expressing untagged ScHmt1 (Sc; pPS1307), CaHmt1 (Ca; pAM390), or ScHmt1 lacking the antenna domain (Scm; pPS2575). CaHmt1 was also expressed in the presence of the PrA vector (−; pNOPPATA). Proteins from mid-log-phase cells were precipitated with IgG-Sepharose. Proteins isolated from 0.5 mg lysate (beads) and 10 μg lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-ScHmt1 antiserum, which also binds to PrA.