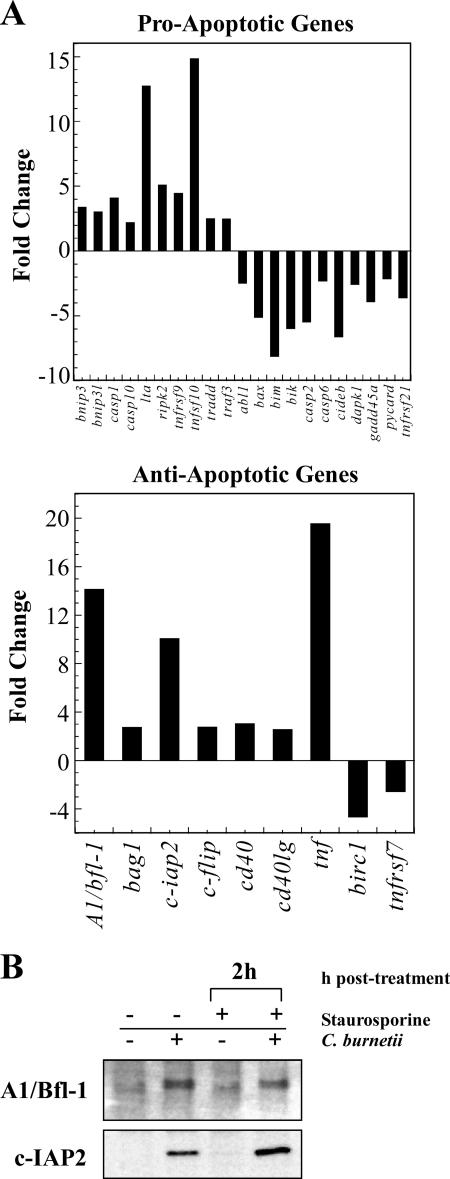
FIG. 6.
C. burnetii infection modulates the expression of apoptosis-related genes. (A) Total RNA was extracted from uninfected THP-1 cells and cells infected with the C. burnetii Nine Mile phase II strain for 48 h. RT-PCR was performed using the RT2 Profiler Array. Genes showing an increase or decrease in expression greater than or equal to twofold relative to uninfected cells are shown. Depicted results are representative of two independent experiments. Twenty-nine genes were up- or down-regulated in response to C. burnetii infection, of which 12 indicated a proapoptotic response and 18 indicated an anti-apoptotic response. (B) THP-1 cells were infected with the C. burnetii Nine Mile phase II strain for 48 h. Infected and uninfected cell cultures were treated with staurosporine for 2 h as indicated. Cells were lysed, and equal amounts of protein were subjected to immunoblot analysis using A1/Bfl-1 or c-IAP2 primary antibodies. Consistent with gene expression data, increased levels of A1/Bfl-1 and c-IAP2 were observed in cell lysates of both untreated and staurosporine-treated infected cell cultures relative to lysates of uninfected cells.