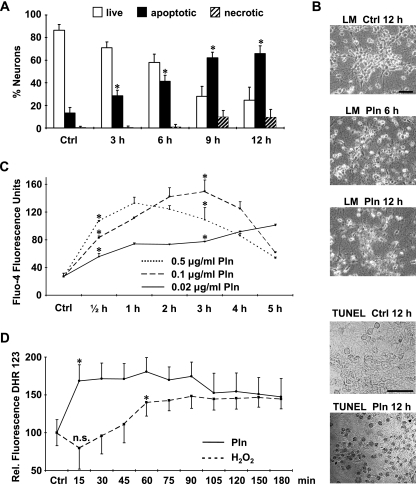
FIG. 1.
Pneumolysin induces increases in intraneuronal calcium and ROS levels and causes cell death. Primary rat cortical neurons were either incubated with pneumolysin (500 ng/ml) or left untreated as a control (Ctrl). (A) Apoptosis and necrosis were differentiated and quantified with the nuclear dyes acridine orange and ethidium bromide. (B) Evidence of apoptosis by light microscopy (LM) and TUNEL of neurons treated with pneumolysin (Pln) (500 ng/ml). Bars, 30 μm. (C and D) Intraneuronal levels of Ca2+ (C) and ROS (D) were visualized by the fluorescence of the dyes Fluo-4 (10 μM) and DHR 123 (10 μM), respectively. Results shown (means + standard deviations) are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate, *, P < 0.05 for comparison with the control by Student's t test; n.s., no significant difference from the control.