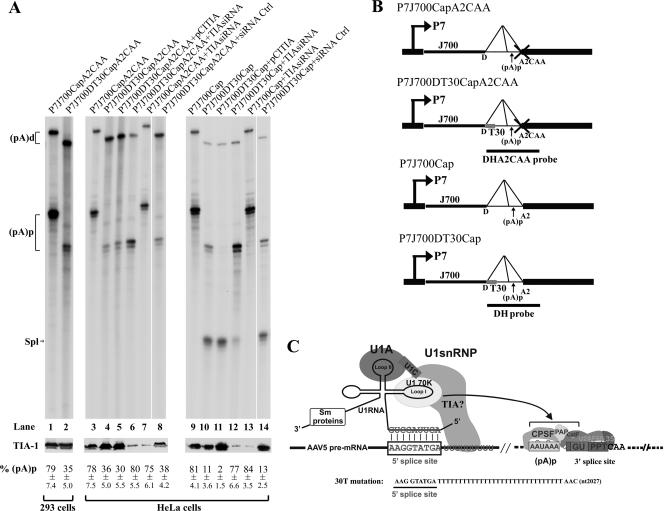
FIG. 4.
Introduction of a putative TIA-1 binding site immediately downstream of the donor site inhibited polyadenylation of the P7-generated RNAs at (pA)p, and modulation of TIA-1 levels in HeLa cells affects the relative ratios of polyadenylation and splicing of P7-generated RNAs. Results are shown for RPAs, using either probe DHA2CAA or probe DH as indicated, of RNA isolated from 293 cells (lanes 1 and 2) or HeLa cells (lanes 3 to 14) transfected with either the splicing-defective plasmid P7J700CapA2CAA (lanes 1, 3, and 7; diagramed in panel B) or P7J700DT30CapA2CAA (lanes 2, 4 to 6, and 8; diagramed in panel B) or the splicing-competent plasmid P7J700Cap (lanes 9 and 13; diagramed in panel B) or P7J700DT30Cap (lanes 10 to 12 and 14; diagramed in panel B), either together with the TIA-1 expression plasmid pCITIA-1 (lanes 5 and 11) or pretransfected with TIA-1 siRNA (lanes 6, 7, 12, and 13) or a control siRNA (lanes 8 and 14). HeLa cells were coinfected with human Ad5 at a multiplicity of infection sufficient to achieve full activity of the AAV5 P7 promoter. Bands representing RNAs that either read through or are polyadenylated at (pA)p are designated (pA)d or (pA)p, respectively. Bands representing RNAs that are spliced are designated Spl. Quantifications of the ratios of P7-generated RNA at (pA)p to total P7-generated RNA are shown as percent (pA)p and are averages of the results for at least three individual experiments, with standard deviations underneath. Shown are expression levels of the TIA-1 protein, as monitored by immunoblotting using a polyclonal anti-human TIA-1 antibody as shown below each RNase protection gel. The predicted interactions between the U1 snRNP and the putative TIA-1 binding site and the mutation introduced into P7J700CapDT30CAA are illustrated in panel C. The curved arrow indicates that the U1 snRNP has an inhibitory effect on polyadenylation at (pA)p. The (pA)p and (pA)d bands protected by RNAs generated from all the plasmids that have the T30 mutation downstream of the donor site were smaller than those protected by RNA generated from the wild-type plasmids. Because the DHA2CAA probe starts a few nucleotides after the donor site, the 30 T mutations present after the donor site are predicted to make both the (pA)p and the (pA)d bands ∼20 nt smaller.