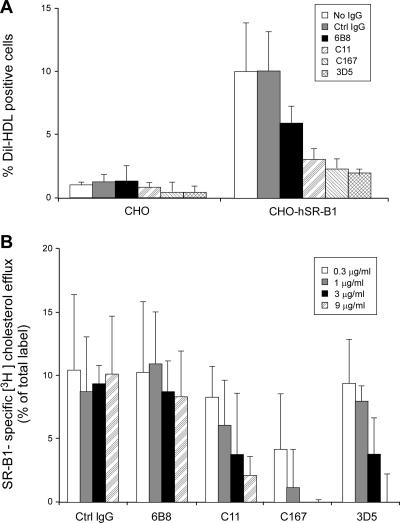
FIG. 3.
Influence of anti-SR-B1 MAbs on HDL binding to SR-B1 and on SR-B1-mediated cholesterol transfer. (A) CHO or CHO/hSR-B1 cells were preincubated in PBS-BSA (no IgG; open bars) or in the presence of control IgG (Ctrl IgG; gray bars) or anti-SR-B1 MAbs (black bars, preincubation with 6B8; hatched bars, preincubation with C11; dotted bars, preincubation with C167; checked bars, preincubation with 3D5) at 5 μg/ml prior to incubation with DiI-labeled HDL (50 μg protein/ml) for 1 h at 4°C. Data are the percentages of DiI-HDL-positive cells. Values are the means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. (B) CHO and CHO/hSR-B1 cells were labeled with [3H]cholesterol, washed, and incubated for 30 min with SFM containing increasing amounts (open bars, 0.3 μg/ml; gray bars, 1 μg/ml; black bars, 3 μg/ml; hatched bars, 9 μg/ml) of control IgG (Ctrl IgG) or anti-SR-B1 MAbs (6B8, C11, C167, and 3D5). After an additional 2 h of incubation in the same medium in the presence HDL (20 μg protein/ml), the amount of [3H]cholesterol present in the medium or remaining in the cells was determined. Data are the percentages of SR-B1-mediated cellular cholesterol efflux and were calculated as the differences between the efflux values determined with CHO/hSR-B1 and those determined with parental CHO cells. Values are the means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments.