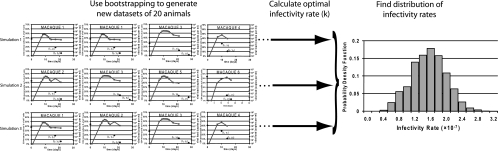
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram of our bootstrapping methodology to obtain an empirical probability distribution for the viral rate of infectivity. We performed 10,000 simulations, and for each simulation, we sampled 20 animals (with replacement) from the pool of 20 macaques to generate a new data set. From each generated data set, we calculated an optimal infectivity rate for the population of animals in the given data set, using the plasma viral load measured in each animal and our mathematical model to predict the infection and death of jejunum CD4+ memory T cells in each sampled animal. We then determined the empirical distribution of the viral infectivity rate from the 10,000 simulations.