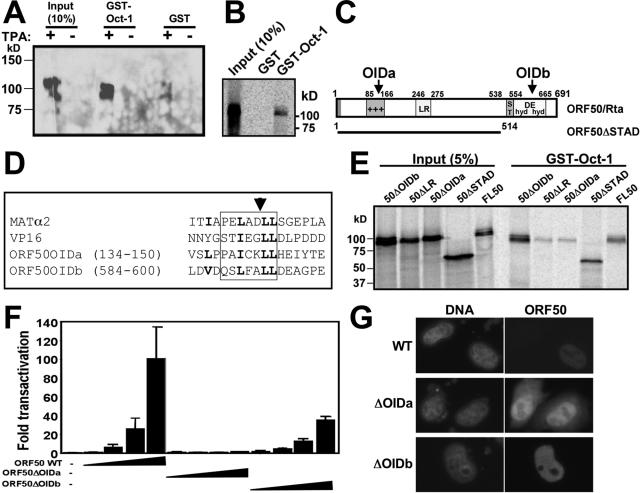
FIG. 4.
The Rta N-terminal basic region contains its OID. (A) GST-Oct-1 binds to the ORF50/Rta protein in extracts from infected cells. GST-Oct-1 or GST alone was immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads and incubated with nuclear extracts from untreated or TPA-treated BCBL-1 cells. Bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Western blotting using anti-Rta primary antiserum. (B) Rta interacts with Oct-1 in vitro. GST pull-downs were performed as described above (A), but 35S-labeled Rta (from programmed RRL) was substituted for nuclear extracts. Following washes, beads were boiled in 2× Laemmli buffer, and bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. Fixed, amplified, and dried gels were analyzed by autoradiography. (C) Two regions of Rta are homologous to homeodomain-interacting regions of VP16 and MATα2. Shown is a schematic of the ORF50/Rta primary amino acid sequence. The region of ORF50 contained within the ORF50ΔSTAD mutant (53) is indicated by the bar below the ORF. Predicted OIDs are indicated with arrows. +++, basic amino acid rich; ST, serine/threonine rich; hyd/DE/hyd, hydrophobic/acidic amino acid repeats. (D) Alignment of OIDs. The sequence of each OID aligned with HSV-1 VP16 and S. cerevisiae MATα2 proteins (45, 82) is shown. The box shows the established or predicted α-helix in the four proteins. The amino acids in OIDa in boldface type indicate positions of site-directed mutations and homology in the aligned domains. The arrowhead indicates the site of the ADPR insertion. Numbers represent amino acid positions. (E) OIDa is required for Rta to bind to Oct-1. GST pull-downs were performed as described above (C). WT and mutant ORF50 constructs were used to program RRLs to make the indicated proteins. Input proteins are shown as a reference. (F) OIDa is required for ORF50/Rta to transactivate the K-bZIP promoter. Expression vectors encoding the indicated proteins were transfected into Akata-31 cells and analyzed for transactivation of the K-bZIP WT reporter plasmid, as described in the legend to Fig. 3A. Amounts of each expression vector were 0, 0.1, 0.5, 2.5, and 12.5 μg. (G) ORF50ΔOIDa and ΔOIDb are expressed in cell nuclei. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated expression vectors and analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence with Rta-specific primary antiserum and fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies. Nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI (4′,6′-diamido-2-phenylindole). Images were converted to grayscale for publication.