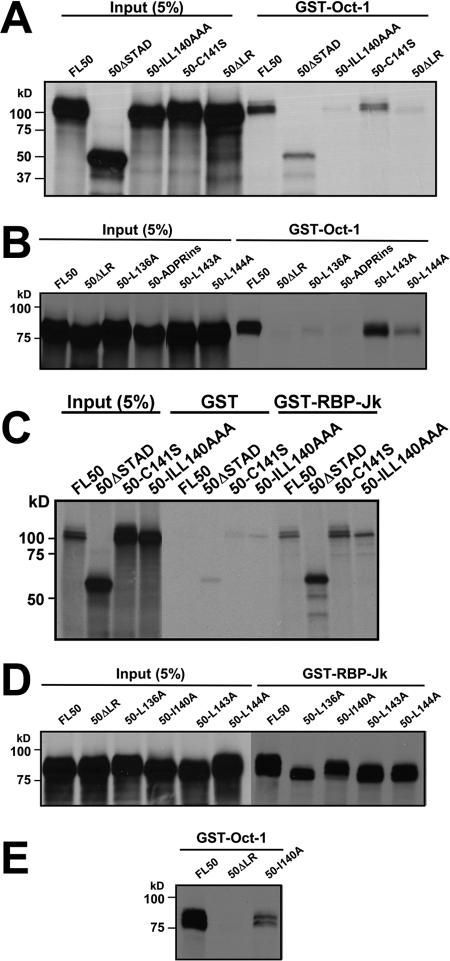
FIG. 5.
Site-specific mutants define the VP16-like amino acid sequence that is essential for the interaction of Oct-1. (A) ORF50-ILL140AAA does not interact with Oct-1 GST. GST pull-downs were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 4E, with RRLs programmed to express the indicated proteins. 50-ILL140AAA contains three alanine substitutions at amino acids 140, 143, and 144; 50-C141S contains a substitution at amino acid 141, changing the Cys to Ser. (B) Additional mutations in OIDa inhibit interactions of ORF50 with Oct-1. GST pull-downs were performed as described above (A) using RRLs programmed to express the indicated ORF50 proteins. (C) ORF50-ILL140AAA retains the ability to interact with RBP-Jk/CSL. GST pull-downs were performed as described above (A) using GST-RBP-Jk immobilized on glutathione beads and the indicated proteins expressed in RRLs. (D) Additional mutations in OIDa have little effect on interactions of ORF50 with RBP-Jk. GST pull-downs were performed as described above (C) using RRLs programmed to express the indicated ORF50 proteins. (E) ORF50-I140A retains a reduced ability to interact with Oct-1. GST pull-downs were performed as described above (B).