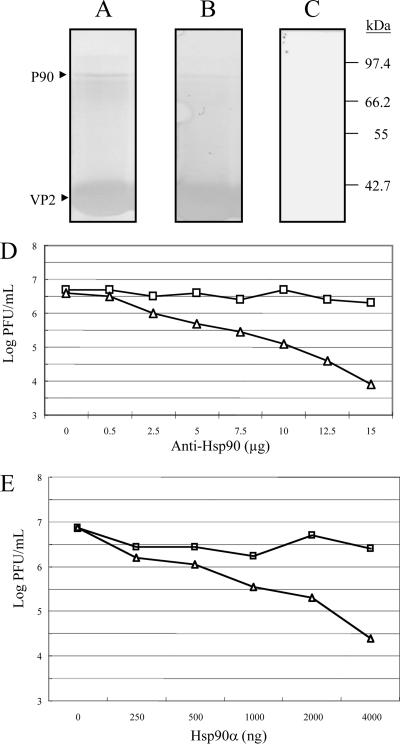
FIG. 7.
VOPBA and far-Western assay of p90 and infection inhibition assays of recombinant Hsp90 protein and anti-Hsp90 in DF-1 cells. Elution fractions containing proteins from DF-1 showing affinity to SVP bound to the immobilized Ni2+ ions were separated by SDS-12.5% PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membranes. Membranes were incubated with (A) or without (C) 2 × 104 PFU of IBDV and later with a rabbit polyclonal anti-VP2 antibody and goat anti-rabbit IgG coupled to alkaline phosphatase; color was developed with BCIP and NBT. A similar procedure was performed for the far-Western assay (B), except that IBDV was replaced with SVP. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the right. p90 (marked with an arrow) from DF-1 cells was recognized by IBDV (A) and SVP (B). Notably, some other proteins were slightly recognized. (D) Infection inhibition assays with anti-Hsp90 antibody. DF-1 cells were preincubated with different concentrations of SVPMAb-1 (square, mouse monoclonal antibody as a control) or anti-Hsp90 antibody (triangle) for 1 h at 4°C. Subsequently, cells were infected with 100 TCID50 of IBDV. Culture supernatants were collected 96 h after infection, and the resulting infectious virus titer was determined. Each point represents the average of two separate experiments. (E) Infection inhibition assays of recombinant Hsp90. Recombinant Hsp90 protein (Hsp90α) of different concentrations or BSA (as a negative control) was preincubated with 100 TCID50 of IBDV for 1 h at 39°C prior to its incubation with DF-1 cells. Culture supernatants were collected 96 h after infection, and the resulting infectious virus titer was determined. Each point represents the average of two separate experiments.