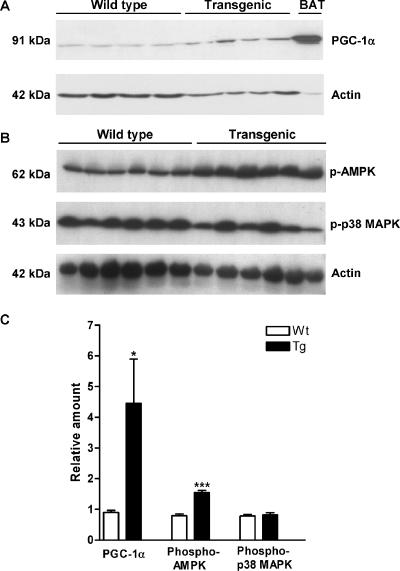
FIG. 6.
PGC-1α, phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK), and phosphorylated p38 MAPK (p-p38 MAPK) protein levels in WAT of SSAT and Wt mice. (A) PGC-1α levels in WAT of 6-month-old female SSAT and Wt mice, detected with a polyclonal antibody against the carboxyl terminus of PGC-1α (Chemicon International, Inc., Temecula, CA). The bottom panel displays actin levels used for normalization. Actin levels were analyzed using a rabbit polyclonal antibody specific for the carboxyl terminus of actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA). The BAT sample in the right-most lane was used as a positive control. (B) p-AMPK and p-p38 MAPK levels in WAT of 6-month-old female SSAT and Wt mice, detected with a polyclonal antibody against the phosphorylated α subunit of AMPK(Thr172) (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA) and a monoclonal antibody against dually phosphorylated p38 MAPK(Thr180/Tyr182) (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA), respectively. The bottom panel displays actin levels used for normalization. Actin levels were analyzed using a rabbit polyclonal antibody specific for the carboxyl terminus of actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA). (C) Relative PGC-1α, p-AMPK, and p-p38 MAPK protein levels in WAT after normalization in SSAT and Wt mice. Results are expressed as means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.