Figure 2.
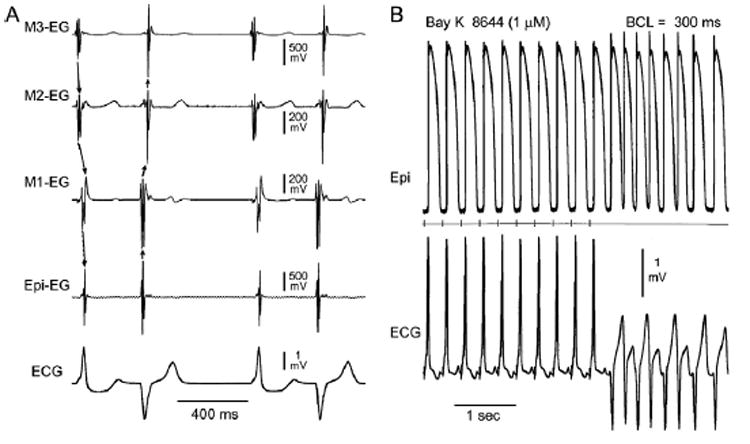
A: BayK8644–induced bidirectional idioventricular rhythm in a left ventricular wedge preparation. Shown are electrograms from epicardial (Epi), subepicardial (M1), midmyocardial (M2), and subendocardial (M3) sites, together with a transmural ECG. BayK8644 (1 μM, 60 minutes of exposure) induces spontaneous bidirectional idioventricular rhythm with ectopic activity alternating between epicardial and endocardial sites of origin. B: BayK8644–induced ventricular tachycardia (VT) of subepicardial origin. Shown are intracellular epicardial (Epi) action potentials and an ECG simultaneously recorded from a left ventricular wedge preparation after 60 minutes of exposure to 1 μM BayK8644. The middle trace is a stimulus marker. VT originating from a subepicardial site developed following a train of 10 stimuli at a basic cycle length (BCL) of 300 ms. T-wave alternans is apparent in stimulated as well as ectopic beats.
