Figure 2.
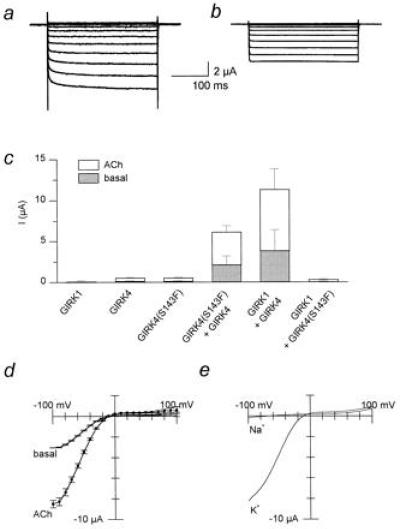
Inclusion of the phenylalanine P-region residue in GIRK4 multimers produces “GIRK1-like” enhancing activity. (a) Coexpression of GIRK1 and GIRK4. (b) GIRK4(S143F) and GIRK4 cRNAs were coinjected. Representative Ba2+-sensitive current traces in the presence of 5 μM ACh are shown for a–c. (c) Current magnitude comparison for GIRK1 (N = 3), GIRK4 (N = 4), GIRK4(S143F) (N = 4), and GIRK4(S143F)/GIRK4 (N = 5), GIRK1/GIRK4 (N = 9), and GIRK4(S143F)/GIRK1 (N = 4). (d) Current-voltage relationships of Ba2+-sensitive GIRK4(S143F)/GIRK4 currents in the absence (basal) or presence of 5 μM ACh from one representative batch of oocytes (n = 5). (e) Representative macroscopic currents (n = 3 oocytes/condition) recorded from oocytes injected with hm2 as well as GIRK4 and GIRK4(S143F) cRNAs in 96 mM KCl in the bath (K) versus 96 mM NaCl (Na) (i.e., KCl-free), in the presence of 5 μM ACh. Currents were obtained by employing a voltage ramp protocol (−100 mV to +100 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV).
