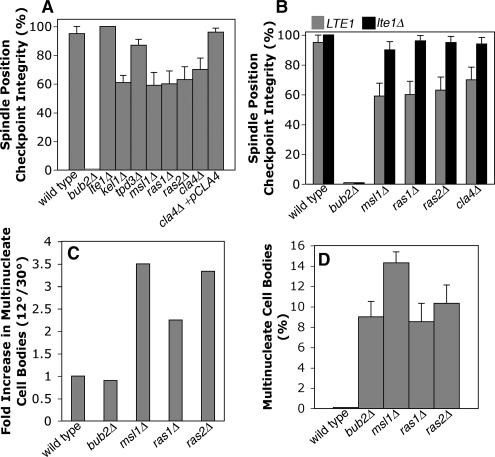
Figure 2.
Spindle position checkpoint in cells lacking Lte1-interacting proteins. (A) Lte1-interacting proteins are required for checkpoint integrity. arp1Δ GFP-TUB1 cells with the indicated additional mutation were assayed for checkpoint integrity. Cells with mispositioned anaphase spindles in the mother were followed by time-lapse movie analysis of GFP-labeled microtubules. The spindle position checkpoint integrity value is the percentage of such cells that remain arrested as opposed to undergoing mitotic exit, revealed by breakdown of the spindle. Mutants lacking Kel1, Msl1, Ras1, Ras2, and Cla4 had defects compared with wild type (p = 0.003, 0.002, 0.003, 0.001, and 0.015, respectively). Error bars, SE of proportion. n ≥ 20 cells for each sample. (B) Deleting LTE1 suppressed the checkpoint integrity phenotype of msl1, ras1, ras2, and cla4 mutants, assayed as in A. In each case, checkpoint integrity was significantly increased by deleting LTE1 (p = 0.003, 0.0002, 0.002, and 0.01, respectively), to levels similar to that of wild type. (C) Checkpoint defects of ras1, ras2, and msl1 mutants were enhanced in the cold. Multinucleate cell bodies were counted, as a percentage of all cells, in asynchronous cultures at 12° and 30°C. The fold-increase at 12 versus 30°C is plotted. n ≥ 281 cells. (D) Multinucleate cell bodies as a percentage of all cells in an asynchronous culture at 12°C. ras1, ras2, msl1, and bub2mutants are similar, suggesting a similar severity in loss of checkpoint.