Figure 2.
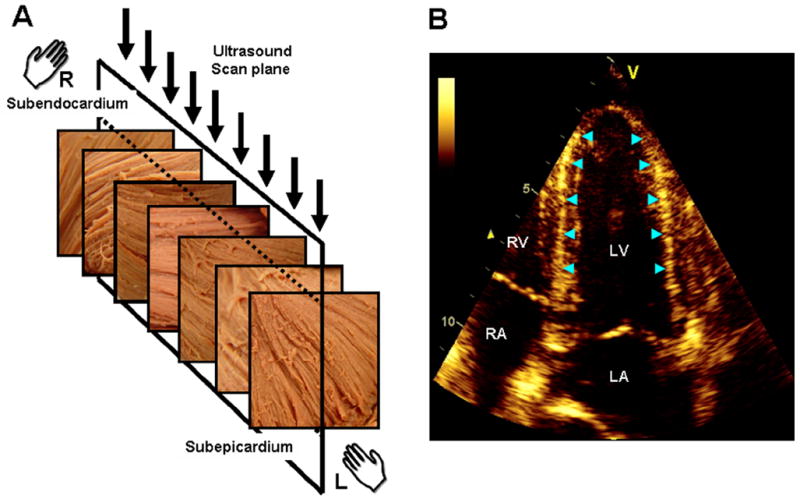
Illustration of the link between the transmural variation of myocardial fiber direction (A) and the speckle pattern generated in echocardiography (B) (adapted from (34)). The fiber direction changes from a right-handed helix in the subendocardium to a left-handed helix in the subepicardium. The direction of myofibers is predominantly circumferential in the midwall. The ultrasonic image plane in apical 4-chamber view (A, arrows) is, therefore, orthogonal to the circumferentially oriented fibers in the midwall. The region of LV wall where fibers are orthogonal to the plane of ultrasound produce bright speckles and can be readily identified in the septum and lateral wall of the LV (B, arrow heads). LV, left ventricle; LA, left atrium; RV, right ventricle; RA, right atrium
