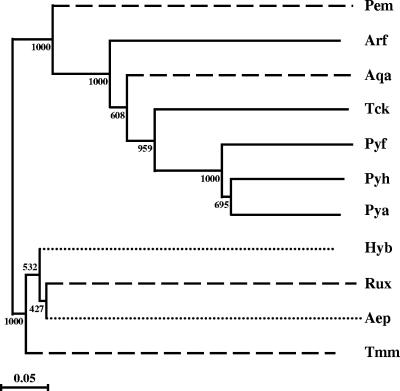
FIG. 6.
Unrooted phylogenetic tree based on available amino acid sequences of IPCT/DIPPS. The ClustalX program (29) was used for sequence alignments and to generate the phylogenetic tree by the neighbor-joining tree construction method. The significance of the branching order was evaluated by bootstrap analysis of 1,000 computer-generated trees. The bootstrap values are indicated. Bar = 0.05 change/site. The species and GenBank accession numbers are as follows: A. fulgidus (Arf; NP_069101), P. furiosus (Pyf; NP_578787); P. horikoshii (Pyh, NP_143114); Pyrococcus abyssi (Pya; NP_126714); R. xylanophilus (EF523341); A. aeolicus (NP_213943); T. kodakaraensis (Tck; YP_184692); A. pernix (Aep; NP_147991 for IPCT and NP_147993 for DIPPS), H. butylicus (Hyb; YP_001012367 for IPCT and YP_001012368 for DIPPS); T. maritima (AE000512 for IPCT and DIPPS); and P. marina (Pem; preliminary sequence data were obtained from The Institute for Genomic Research through the website at http://www.tigr.org). Bacteria, euryarchaeotes, and crenarchaeotes are distinguished by using dashed, solid, and dotted lines, respectively.