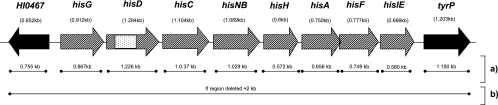
FIG. 1.
Genomic map of the his operon in strain Rd. □, location of sJPX132;▒, genes deleted in 23221 (throat strain) but present in G622 (middle ear strain) and Rd; ▪, genes present in 23221 (throat strain), G622 (middle ear strain), and Rd. (a) PCR protocol for each individual his gene and the flanking genes to determine size of insertion/deletion; (b) PCR protocol spanning the his region, used to verify size and location of the his indel. If an isolate is missing the complete his operon, a 2-kb product is amplified. If an isolate has the complete his operon, then a negative PCR will result, because the genomic region is too large to amplify (10.2 kb) using traditional PCR techniques.