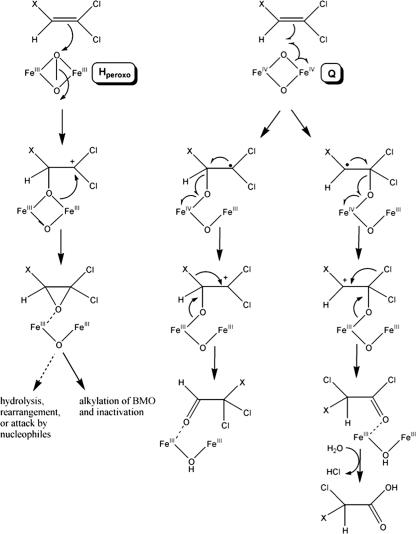
FIG. 3.
Proposed oxidative pathway of 1,1-DCE or TCE with BMO. X represents either Cl or H. Oxidation by the peroxodiiron(III) intermediate (Hperoxo) occurs by a two-electron transfer step and results in epoxide formation. Oxidation by the di(μ-oxo)diiron(IV) intermediate (Q) initiates at either carbon, with electron transfer forming a cationic intermediate. The cationic intermediate may alkylate the active site, resulting in enzyme inactivation, or leads to a chloride or hydride shift. Wild-type BMO primarily utilizes the Hperoxo enzyme intermediate for CE oxidation, and mutant strain G113N primarily utilizes the Q enzyme intermediate.