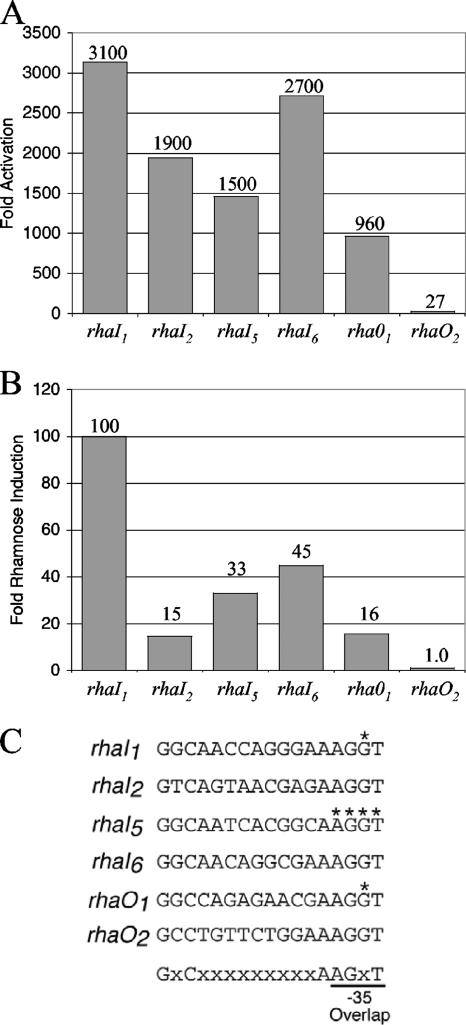
FIG. 5.
In vivo transcription activation by His6-RhaS-CTD or RhaS. The indicated RhaS half-sites, in the context of Φ(rhaB-lacZ)Δ66 on multicopy plasmids (pSE276 and derivatives), were assayed for β-galactosidase activity. Cells were grown in TY medium. (A) Activation by His6-RhaS-CTD, expressed from pSE271 in SME1051 [Δ(rhaSR)]. Activation (fold) was determined by dividing the activity obtained with RhaS-CTD by the activity of pSU18 alone (vector only) at each promoter. The activity of pSU18 alone ranged from 0.39 to 0.99 Miller units. (B) Transcription activation by RhaS expressed from the chromosome in SME1048 (wild-type rhaSR). Rhamnose induction (fold) was determined by dividing the activity of each fusion in the presence of rhamnose by the activity of the same fusion in the absence of rhamnose. The activities in the absence of rhamnose ranged from 0.21 to 0.29 Miller units. (C) The DNA sequences of the half-sites used in these experiments are shown. The asterisks indicate positions at which base pairs were changed from the wild-type half-site sequences (see Fig. 1) so that the DNA sequence of the overlapping −35 element was not changed. The bottom line indicates the sequence and position of the 6 important bp in the RhaS binding site that were used to identify rhaO1 and rhaO2.