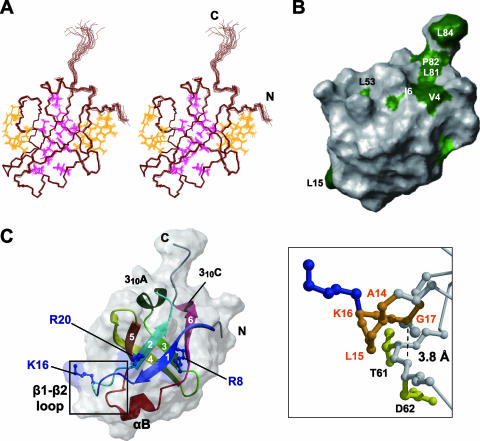
FIG. 3.
Tertiary structure of RimM.1-85. (A) Stereo view illustrating a trace of the backbone atoms for the ensemble of the 20 structures with the lowest CYANA target function of RimM.1-85. Interior and exterior side chains that stabilize the RimM.1-85 structure are shown in magenta and orange, respectively. The colors of these side chains correspond to those of the triangles in Fig. 1B. (B) Mapping of hydrophobic residues on the molecular surface of RimM.1-85, generated by the MOLMOL (23) program. This structure is rotated by 60° around the y axis, as in panel A. Conserved hydrophobic residues among bacterial RimM proteins are colored green, and conserved but exposed hydrophobic residues are dark green. A large number of conserved hydrophobic residues are invisible, suggesting that they are deeply buried in the core. (C) Ribbon representation of the RimM.1-85 structure (left) in the same orientation as in panel A. The strands in the β-sheet are indicated by arrows, and the secondary structure elements are labeled. The side chains of the three conserved basic residues (blue) are linearly arranged on the surface of RimM.1-85. Right, enlarged view of the framed area of the left panel. The highly conserved segment in the β1-β2 loop, which has been regarded as the GXXG motif, is represented as an orange ball-and-stick model. Some of the residues relevant to the discussion are labeled. The broken line represents the distance between the α-carbon atom of G17 and the nitrogen atom of D62.