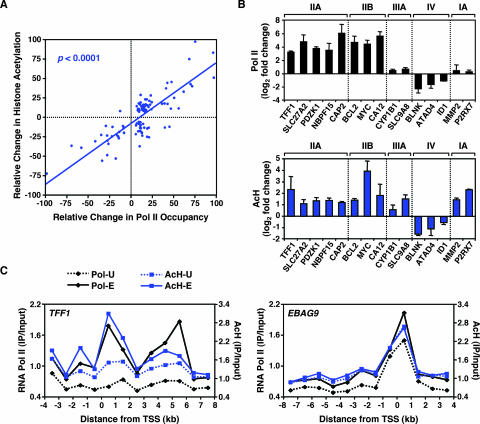
FIG. 4.
RNA Pol II occupancy correlates with histone acetylation at the promoters of E2-regulated genes. (A) Correlation between E2-dependent RNA Pol II recruitment and histone H3 and H4 acetylation. The relative change in histone acetylation or Pol II occupancy is defined as the log2 change (n-fold) upon E2 treatment as a percentage of the maximum log2 change (n-fold) observed for each factor. The correlation coefficient is 0.73 (P < 0.0001). All array elements with significant ChIP enrichment ratios (P < 0.05) were included in the analysis. (B) Validation by ChIP-qPCR of the ChIP-chip results for selected promoters from the estrogen-regulated promoter array. Results for RNA Pol II (upper graph; black) and AcH (lower graph; blue) are shown. The class IIA, IIB, IIIA, IV, and IA promoters are as shown in Fig. 2C. Each bar represents the mean + SEM for at least three separate determinations. (C) ChIP-chip tiling for the TFF1 and EBAG9 genes. Occupancy, expressed as ChIP enrichment ratios (IP/input), for RNA Pol II and AcH throughout the indicated genomic region is shown in the absence (-U) or presence (-E) of E2. “0” represents the TSS; regions upstream of the TSS are indicated by negative numbers.