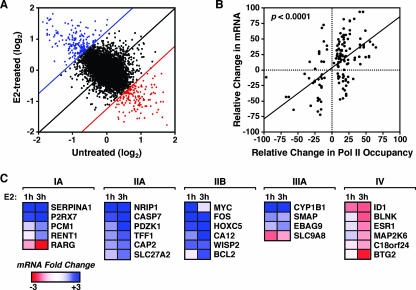
FIG. 6.
E2-dependent gene expression correlates with RNA Pol II recruitment to target promoters. (A) RNA expression analysis of MCF-7 cells in the presence or absence of a 3-h treatment with E2 by use of Affymetrix U133A 2.0 microarrays. Scatterplot presentation of normalized signal for each gene on the microarray in E2-treated cells (y axis) plotted versus the signal for each gene from untreated cells (x axis). The blue and red lines represent the twofold increase or decrease cutoffs for expression, respectively. Genes showing E2-dependent increases in expression are in blue, whereas genes showing E2-dependent decreases in expression are in red. Genes regulated less than twofold by E2 are in black. (B) Correlation between E2-dependent RNA Pol II recruitment and mRNA expression. The relative change in mRNA or Pol II occupancy is defined as the log2 change (n-fold) upon E2 treatment as a percentage of the maximum log2 change (n-fold) observed for each factor. The correlation coefficient is 0.45 (P < 0.0001). All promoters showing significant changes (P < 0.05) for RNA expression and RNA Pol II ChIP recruitment were included in the analysis. (C) Gene-by-gene confirmation of expression microarray results. MCF-7 cells were treated with or without E2 for 1 h or 3 h, and then RNA was isolated and analyzed by qPCR for genes in classes IA, IIA, IIB, IIIA, and IV (from Fig. 2C). The mRNA expression scale is shown.