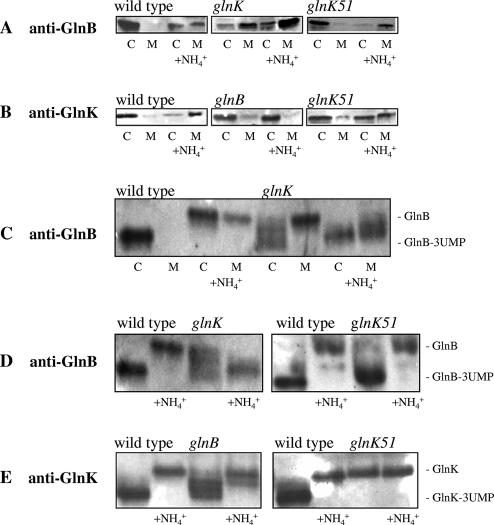
FIG. 3.
Interaction of PII homologs with the membrane in glnK and glnB mutants. Two parallel cultures of the R. capsulatus wild type (B10S) and glnB (PHU332), glnK (BSRUB13), and glnK51 (GlnK-Y51F; BSRUB13/pAP2) mutants were grown under N2-fixing conditions. NH4Cl (1 mM) was added to one of the parallel cultures 15 min prior to harvest. Cytoplasmic (C) and membrane (M) fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE (5 μg of total protein loaded per well) and Western immunoblotting with anti-GlnB (A) or anti-GlnK (B) antibody. Cytoplasmic (C) and membrane (M) fractions of the wild type (B10S) and glnK mutant (BSRUB13) were subjected to native PAGE (5 μg of total protein loaded per well) followed by Western immunoblotting with anti-GlnB antibody (C). Whole-cell extracts from cultures of the wild type (B10S) and glnB (PHU332), glnK (BSRUB13), and glnK51 (GlnK-Y51F; BSRUB13/pAP2) mutants exposed or not for 15 min to 1 mM NH4Cl were analyzed by native PAGE (5 μg of total protein loaded per well) and Western blotting (5 μg of total protein was loaded per well) with anti-GlnB (D) or anti-GlnK (E) antibody.