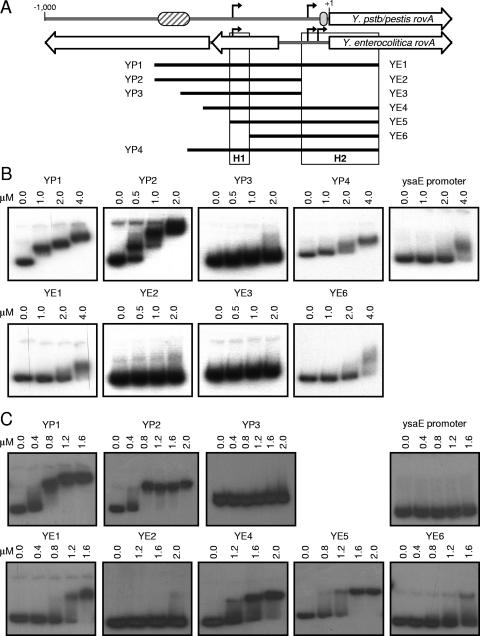
FIG. 5.
Ability of RovA and H-NS to bind to the rovA promoters. (A) Schematic representation of the rovA promoters from Y. pseudotuberculosis/Y. pestis (Y.pstb/pestis rovA) and Y. enterocolitica and the PCR products used in EMSA analysis. The striped and gray ovals represent the predicted high-affinity RovA/H-NS and predicted low-affinity RovA binding sites, respectively, from Y. pseudotuberculosis. The black arrows represent transcriptional initiation sites. The black bars represent PCR products used for the EMSA from Y. pseudotuberculosis/Y. pestis (YP) and Y. enterocolitica (YE). H1 and H2 represent regions of H-NS binding in the Y. enterocolitica promoter. (B) EMSA performed with recombinant RovA-His. (C) EMSA performed with recombinant H-NS-His. The fragment used in each panel and the concentrations of the protein added to each reaction mixture are shown. The ysaE promoter is not regulated by either RovA or H-NS and was included as a negative control for binding.