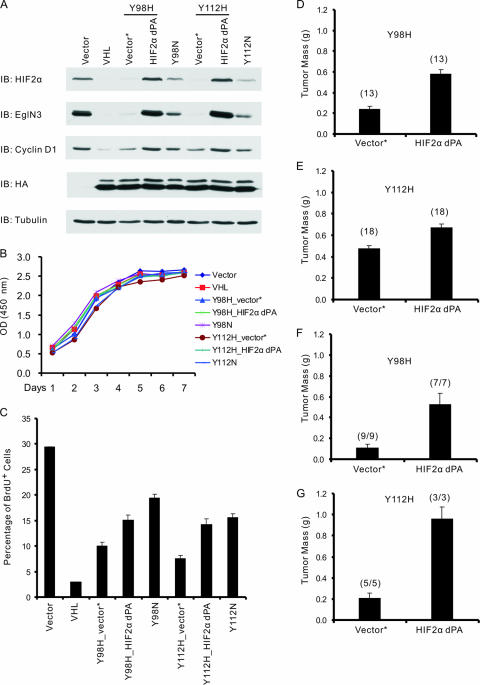
FIG. 5.
Stabilizing HIF2α promotes tumor growth by 786-O cells producing type 2A pVHL mutants in vivo. (A) Immunoblot (IB) analysis of 786-O renal carcinoma cells infected with retroviruses encoding the indicated HA-tagged pVHL proteins or with the empty vector (Vector). Where indicated, cells were also infected with a second virus encoding HIF2α dPA (P405A/P531A) or with the corresponding empty virus (Vector*). (B) Optical density (OD) at 450 nm, which reflects viable cell number, of 786-O cells studied in panel A and maintained in 10% fetal bovine serum. The standard deviation is <0.2 for all data points. (C) BrdU incorporation of 786-O cells stably infected with retroviruses as in panel A and maintained in serum-free DMEM supplemented with 1% insulin-transferrin-selenium (1% ITS) for 72 h prior to BrdU pulse for 2 h. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (D and E) Masses of tumors formed by 786-O cells stably infected with retroviruses as in panel A 8 weeks after subcutaneous injection in nude mice. Each mouse was injected with the corresponding empty virus (Vector*) or HIF2α dPA cells on opposite flanks. The number of tumors analyzed is indicated in parentheses. Error bars are 1 standard error of the mean (P < 0.05). (F and G) Calculated masses of tumors formed by 786-O cells stably infected with retroviruses as in panel A 10 weeks (Y98H) or 9 weeks (Y112H) after intraparenchymal renal injection in nude mice. The presence of tumor cells was confirmed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. The tumor mass was calculated by subtracting the mass of the left kidney (normal) from the mass of the right kidney (implanted with tumor). Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of animals with tumors divided by number of animals injected. Error bars are 1 standard error of the mean (P < 0.05).