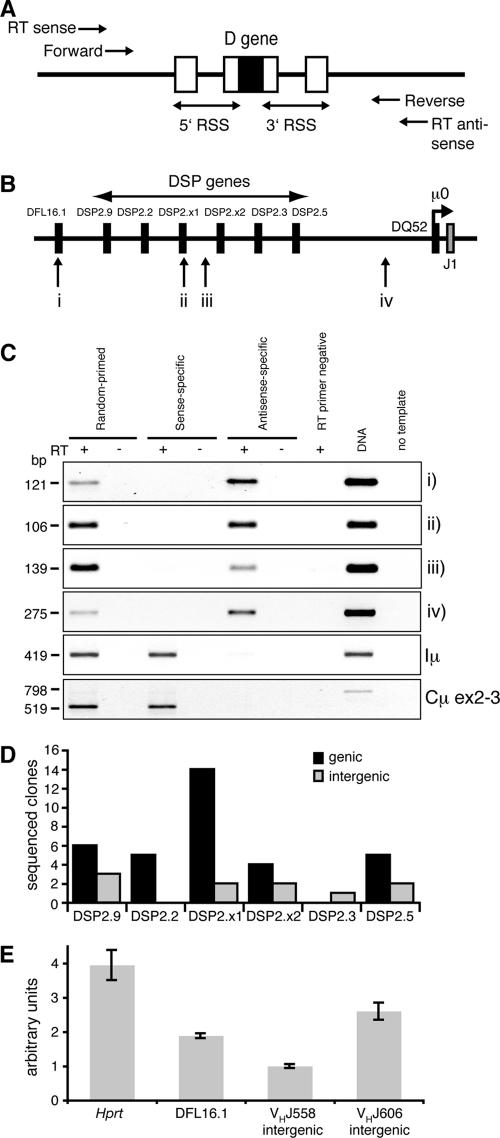
FIG. 2.
Detection of germ line transcription across the Igh D region. (A) Design of the DH region germ line transcription reverse transcription-PCR assay. Reverse transcription antisense (to detect sense transcription) and sense (to detect antisense transcription) primers were designed 5′ and 3′ of the DH gene RSS sequences. Nested primers were used for PCR. Similar schemes were used for intergenic regions. (B) Schematic of the DFL16.1-J1 sequence showing regions analyzed by reverse transcription-PCR. Not to scale. (C) Reverse transcription-PCR of Rag1−/− CD19+ total RNA. Above lanes, with (+) or without (−) reverse transcriptase (RT). Right margin, regions amplified (shown in panel B); left margin, molecular sizes. DNA, genomic DNA positive control. (D) Sequencing of DSP genic and intergenic reverse transcription-PCR products. The number of reverse transcription-PCR products cloned and sequenced is shown for each DH gene and intergenic region. (E) Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR of Rag1−/− CD19+ random-primed cDNA showing relative transcription levels for Hprt, DFL16.1, VHJ558 intergenic, and VHJ606 intergenic regions. The level of VHJ558 intergenic transcription was arbitrarily set to 1.