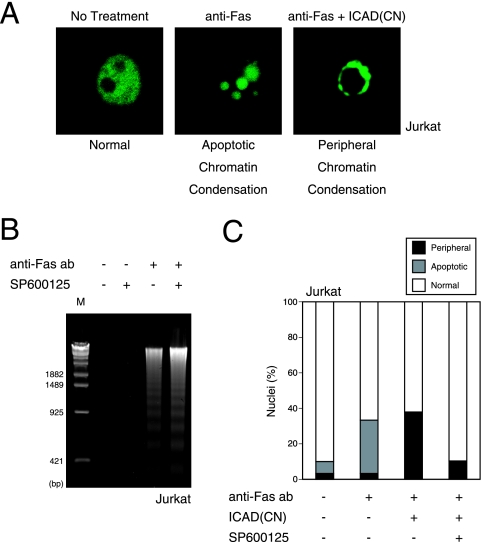
FIG. 6.
JNK activity is involved in peripheral chromatin condensation during Fas-mediated apoptosis. (A) Discrimination between stages I and II of chromatin condensation. Jurkat cells were transfected with either control vector or vector expressing ICAD-CN. After 21 h, cells were left untreated or treated with 100 ng/ml anti-Fas Ab for 4 h to induce apoptosis, and nuclei were examined by CLSM. In the absence of ICAD cleavage, chromatin condensation remained at stage I (peripheral chromatin condensation) instead of completing stage II (apoptotic chromatin condensation). (B) JNK inhibition does not affect anti-Fas-induced DNA fragmentation. Jurkat cells were treated for 4 h with 100 ng/ml anti-Fas Ab in the presence of solvent alone (0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide) or 5 μM JNK inhibitor SP600125. Nucleosomal DNA fragmentation was then examined as described in the legend of Fig. 4A. (C) JNK inhibition blocks anti-Fas-induced peripheral chromatin condensation in Jurkat cells expressing ICAD. Jurkat cells were transfected with control vector or ICAD-CN. After 21 h, transfected cells were treated for 4 h with anti-Fas Ab and SP600125 as described for panel B. Nuclei were examined by CLSM. The data are expressed as the percentages of cells with nuclei showing normal morphology, apoptotic chromatin condensation, or peripheral chromatin condensation, as exemplified in panel A.